-
 Wheel Hub Bearings
Wheel Hub Bearings -
 Wheel Hub Bearings
Wheel Hub BearingsDAC387436 DAC458045 Hub Deep Groove Ball Car Wheel Bearing
-
 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsFL204 FL205 FL206 Stainless Steel Pillow Block Bearing
-
 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsT204 T207 UC204 High Speed Insert Pillow Block Bearing
-
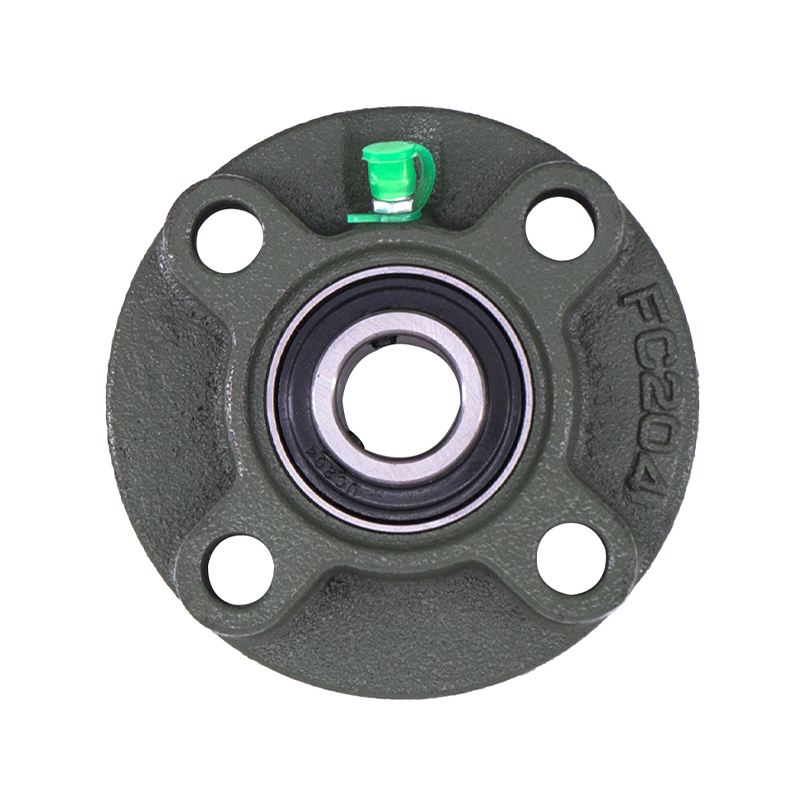 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsFC204 F210 Auto Wheels Bike Pillow Block Bearing
-
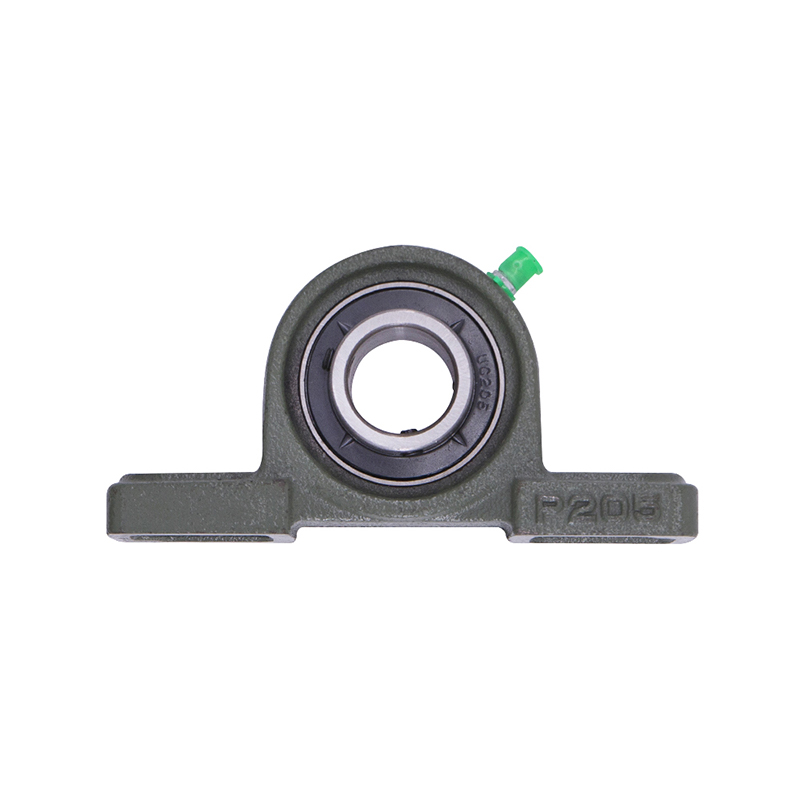 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsP207 206 205 203 High Precision Wheel Pillow Block Bearing
-
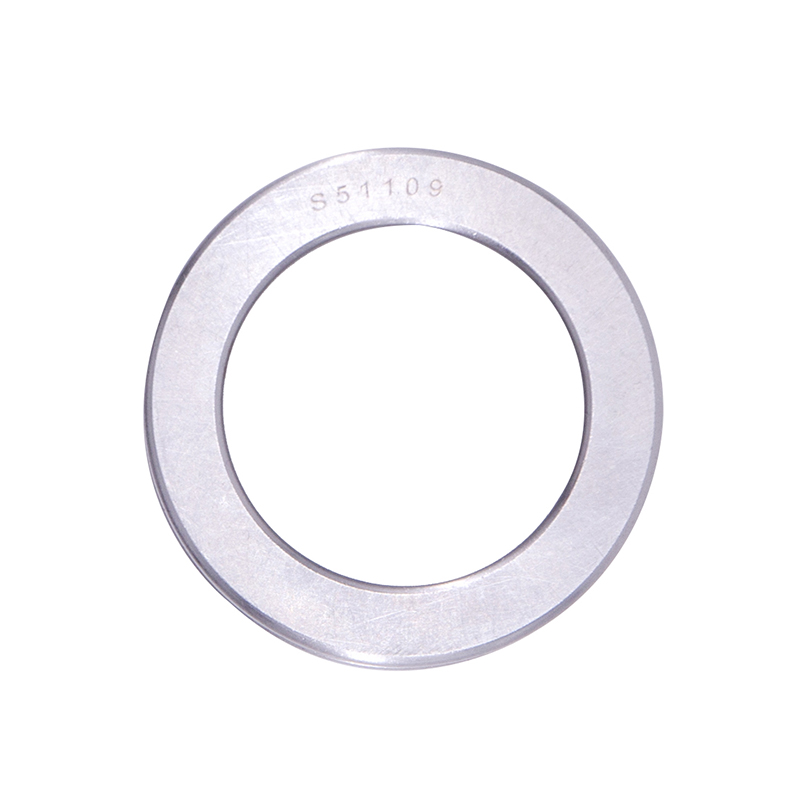 Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust Roller BearingsS51100 S51107 S51109 Car Wheel Plain Thrust Ball Bearing
-
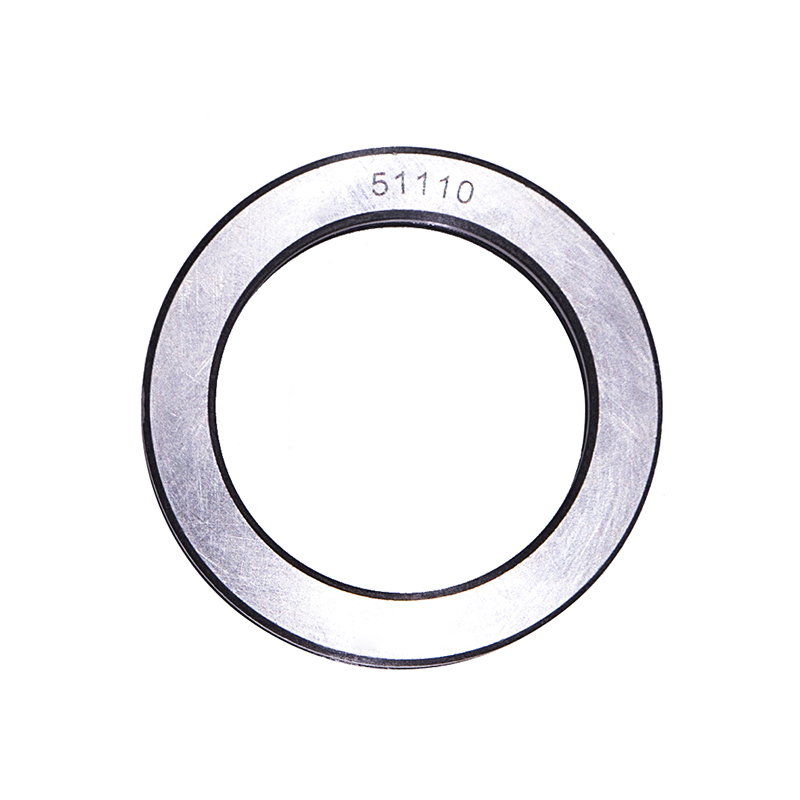 Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust Roller Bearings51110 51107 51104 51206 High Speed Plain Thrust Ball Bearing
Ball Bearings: How to Choose Them
Industry news-Ball bearings factory are essential mechanical components used in a wide range of applications, from household appliances to industrial machinery. They reduce friction between rotating parts, support radial and axial loads, and ensure smooth motion.

Importance of Ball Bearings
Ball bearings are integral to the performance of rotating machinery. By friction between moving parts, they help reduce wear and tear, improve energy efficiency, and enhance the lifespan of equipment. They are commonly used in electric motors, bicycles, automobiles, conveyor systems, and industrial machines. Selecting the right ball bearing ensures reliable operation, consistent performance, and reduced maintenance costs.
Key Characteristics of Ball Bearings
Several characteristics define the performance and suitability of ball bearings:
1. Load Capacity
Ball bearings are designed to support both radial and axial loads. Radial loads act perpendicular to the shaft, while axial loads act parallel. Standard ball bearings typically handle moderate radial and axial loads, while specialized designs such as angular contact ball bearings can accommodate higher axial loads in one or both directions.
2. Size and Dimensions
Ball bearings come in various sizes and dimensions, including inner diameter, outer diameter, and width. Choosing the correct size ensures proper fit within machinery, smooth rotation, and balanced load distribution. Standardized sizing makes it easier to replace or upgrade bearings when needed.
3. Material
Ball bearings are commonly made from high-quality steel, such as chrome steel or stainless steel. Chrome steel offers high strength and wear resistance, while stainless steel provides corrosion resistance for applications in humid or wet environments. Ceramic balls are also available for high-speed applications, offering lower friction, lighter weight, and longer service life.
4. Cage Type
The cage, or retainer, keeps the balls evenly spaced within the bearing. Common cage materials include steel, brass, and synthetic polymers. The cage type influences operating speed, noise levels, and durability. For example, polymer cages are quieter and lighter, while brass cages offer higher strength and temperature resistance.
5. Seals and Shields
Sealed or shielded ball bearings help prevent contamination from dust, moisture, or other particles. Shields allow some airflow and are suitable for high-speed applications, while sealed bearings provide better protection for environments where debris or fluids may be present. Choosing the correct sealing option ensures longer service life and lower maintenance.
6. Speed Capability
Ball bearings are rated for operating speeds. High-speed applications, such as electric motors or precision instruments, require bearings designed to handle rotational speeds without overheating or excessive wear. Proper lubrication is also crucial for maintaining high-speed performance.
7. Noise and Vibration
Noise and vibration levels are important in applications such as household appliances, fans, and precision machinery. Bearings with smooth surfaces, proper lubrication, and well-designed cages minimize operational noise and vibration, enhancing overall performance and user comfort.
How to Choose Ball Bearings
Selecting the right ball bearing requires consideration of several factors:
Load Requirements: Determine the radial and axial loads the bearing must support. Standard bearings are suitable for moderate loads, while angular contact or thrust ball bearings are ideal for higher axial loads.
Operating Speed: Match the bearing’s speed rating to the machinery’s rotational speed. High-speed applications may benefit from ceramic or precision-grade steel bearings.
Environmental Conditions: Consider exposure to moisture, dust, or chemicals. Stainless steel or sealed bearings are preferred for humid or corrosive environments.
Space and Size Constraints: Ensure the bearing fits properly within the available space, maintaining correct alignment and load distribution.
Maintenance Considerations: Sealed or shielded bearings reduce the need for frequent lubrication and maintenance, while open bearings may require periodic servicing.
Noise Sensitivity: For quiet applications, select bearings with polymer cages, shields, and smooth ball surfaces to reduce operational noise.
Applications of Ball Bearings
Ball bearings are versatile and widely used in:
Electric motors and generators
Automotive wheels, gearboxes, and engines
Household appliances such as washing machines and fans
Conveyor systems and industrial machinery
Bicycles and motorcycles for smooth rotation and handling

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español
