-
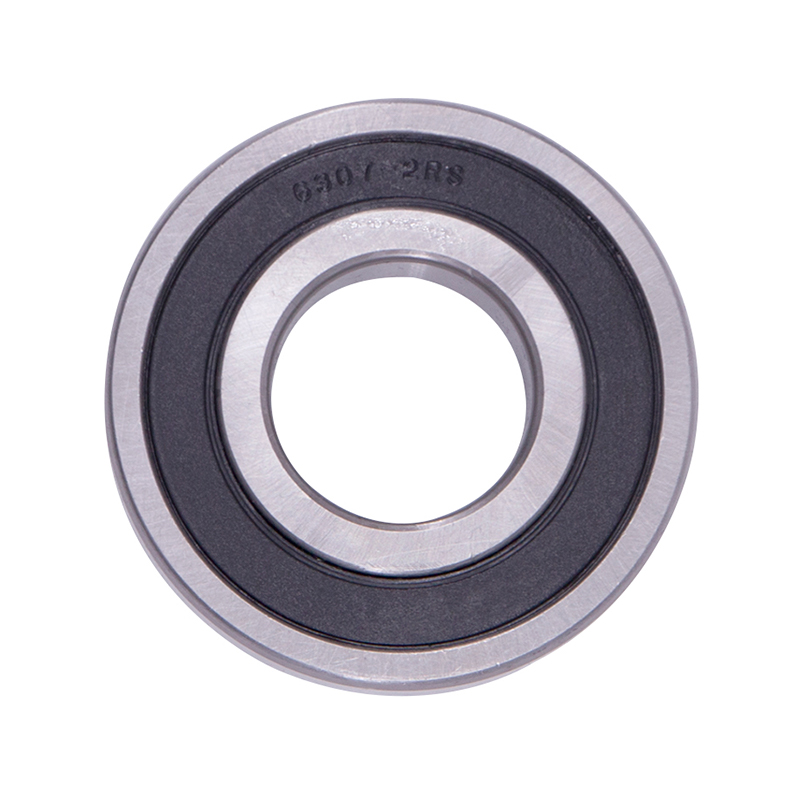 Wheel Hub Bearings
Wheel Hub Bearings -
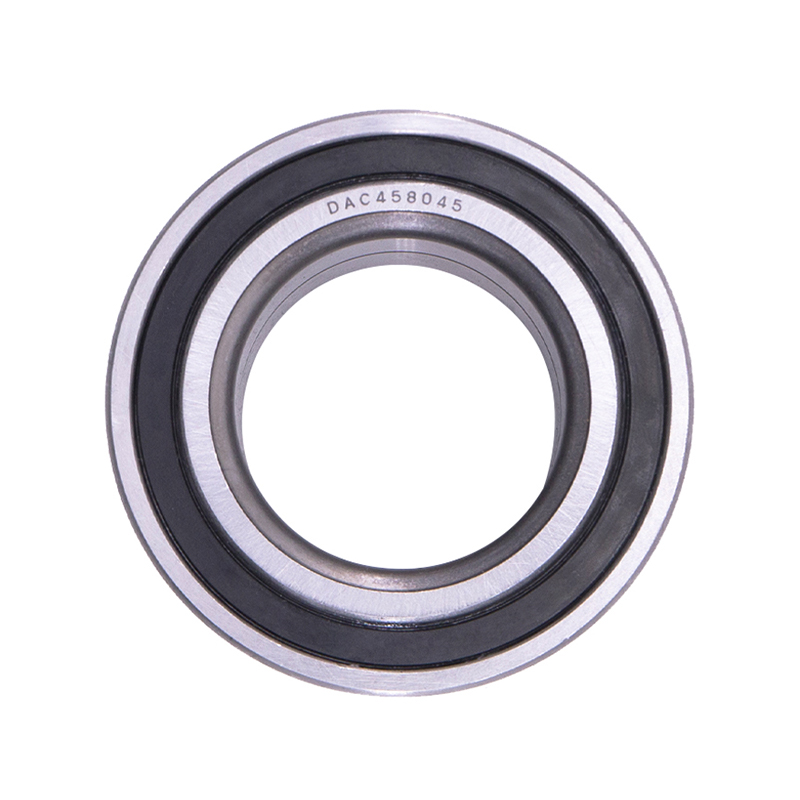 Wheel Hub Bearings
Wheel Hub BearingsDAC387436 DAC458045 Hub Deep Groove Ball Car Wheel Bearing
-
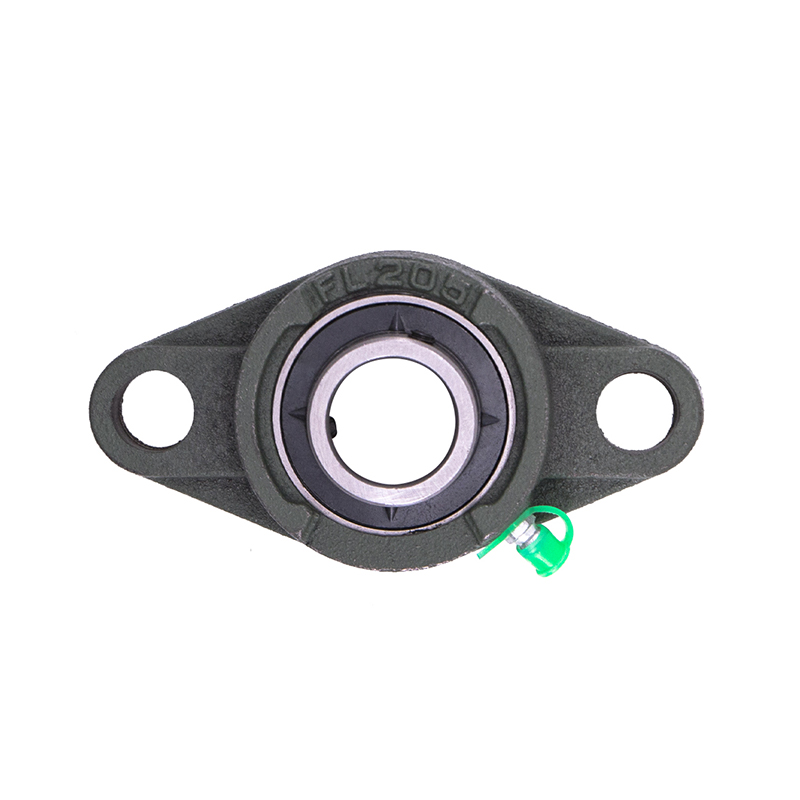 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsFL204 FL205 FL206 Stainless Steel Pillow Block Bearing
-
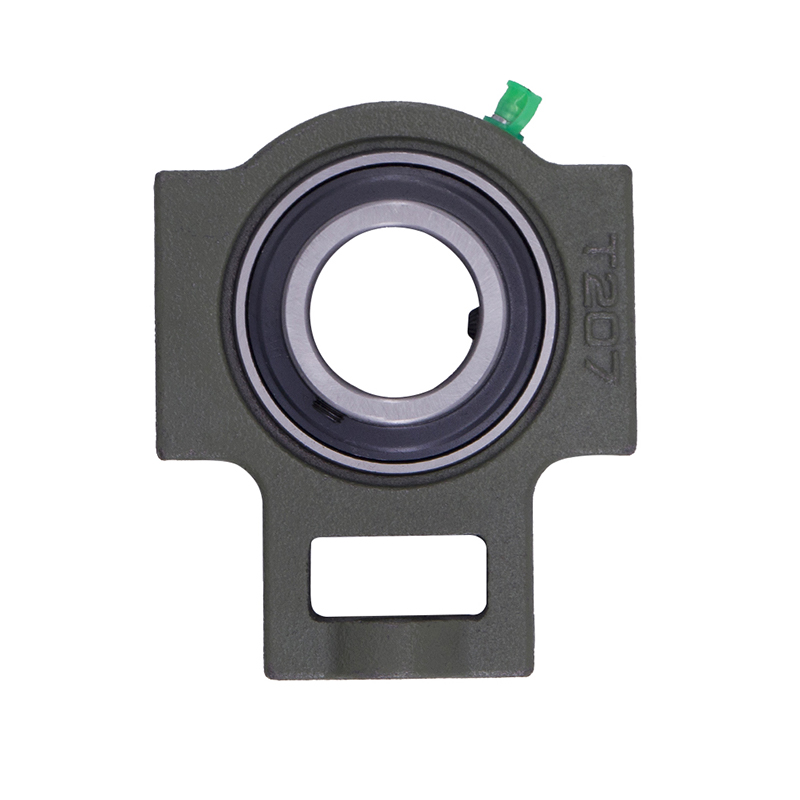 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsT204 T207 UC204 High Speed Insert Pillow Block Bearing
-
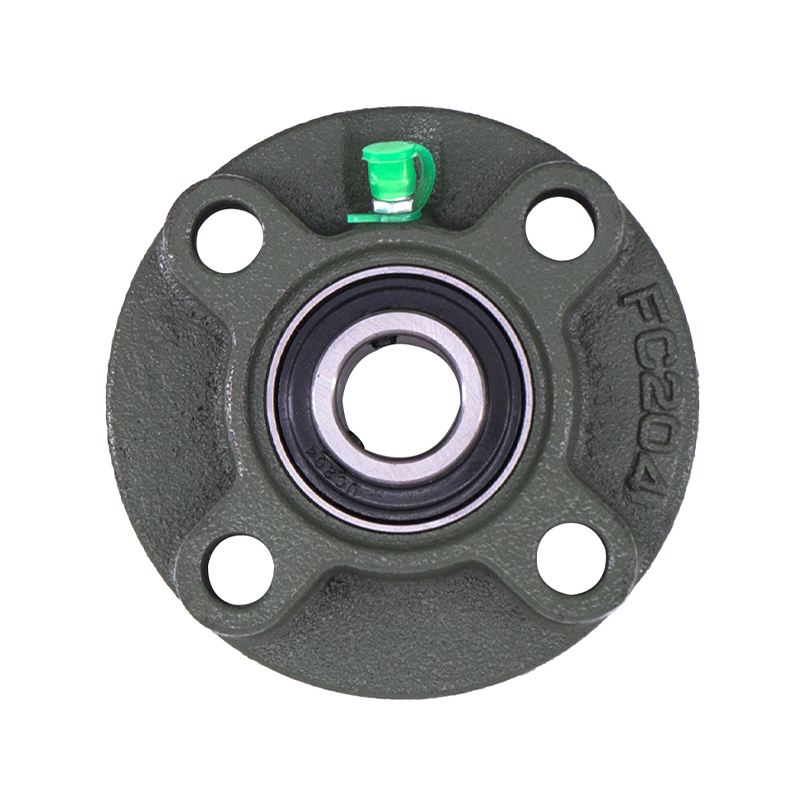 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsFC204 F210 Auto Wheels Bike Pillow Block Bearing
-
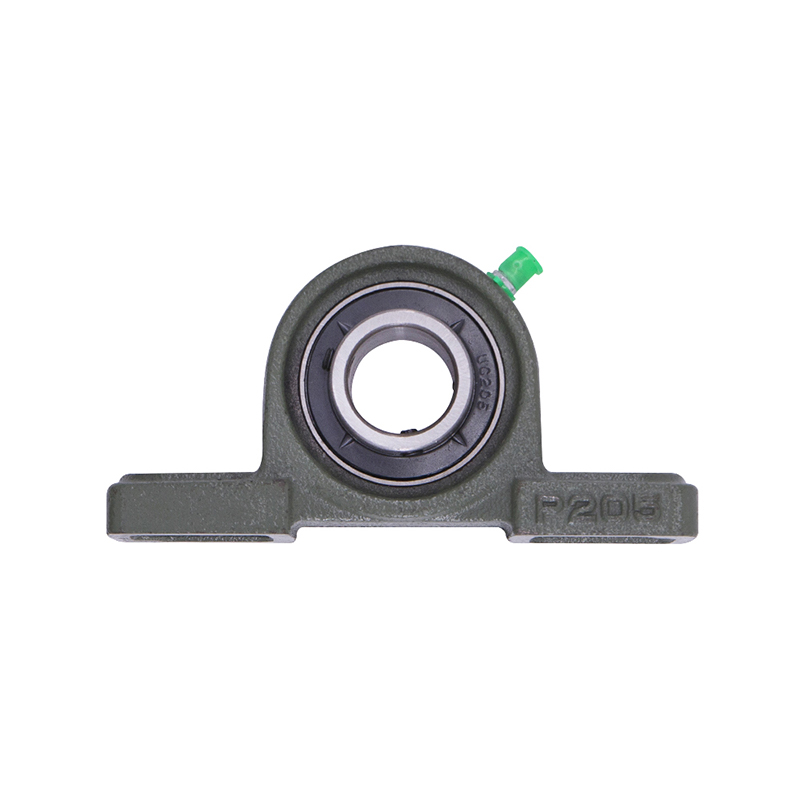 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsP207 206 205 203 High Precision Wheel Pillow Block Bearing
-
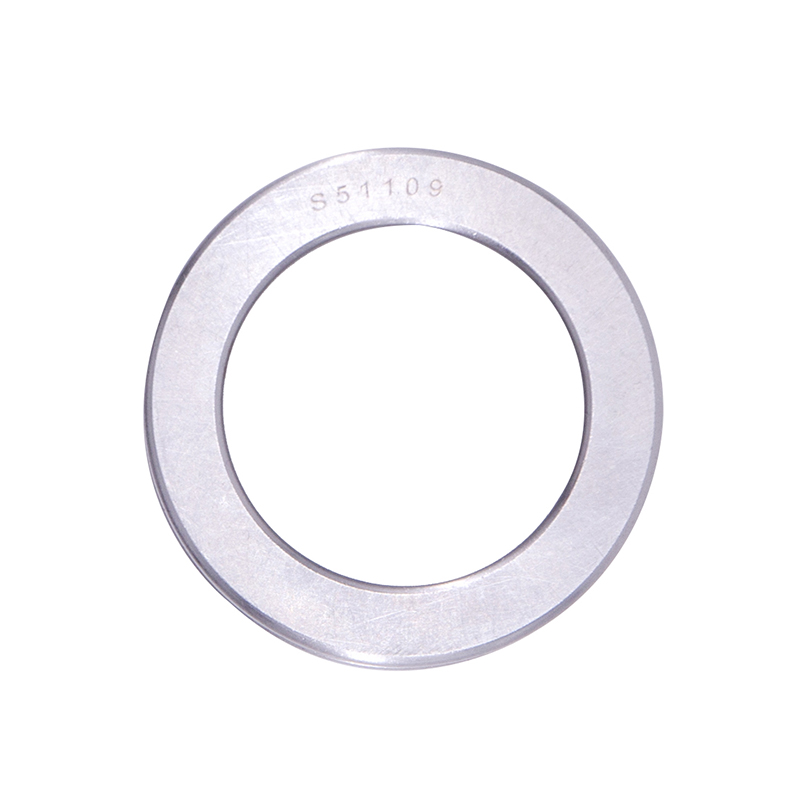 Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust Roller BearingsS51100 S51107 S51109 Car Wheel Plain Thrust Ball Bearing
-
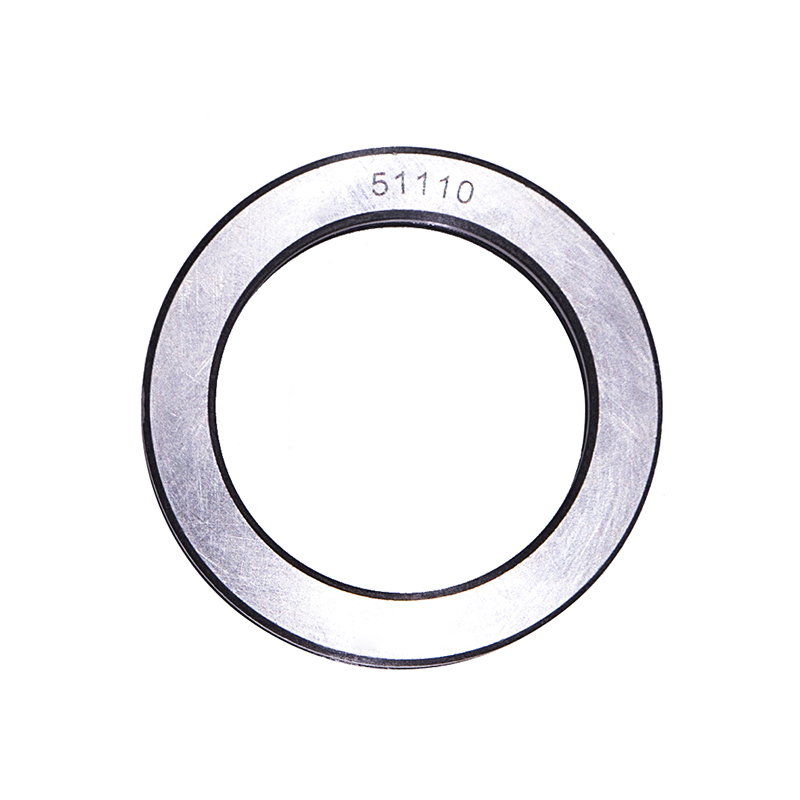 Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust Roller Bearings51110 51107 51104 51206 High Speed Plain Thrust Ball Bearing
Methods to Improve the Life of Deep Groove Ball Bearings
Industry news-Deep groove ball bearings are one of the widely used bearing types due to their versatility, simplicity, and cost-effectiveness. They are essential components in a wide range of applications, including electric motors, household appliances, automotive systems, and industrial machinery. Despite their robust design, the performance and lifespan of deep groove ball bearings can be significantly affected by several operational and environmental factors. Therefore, improving their life through optimized design, material selection, lubrication, and handling processes is crucial for reliability and efficiency in any mechanical system.

Material Selection and Heat Treatment
The step in ensuring the durability of deep groove ball bearings is the selection of high-quality materials. Bearings are typically made from high carbon chromium steel (commonly known as bearing steel) due to its strength, hardness, and wear resistance. For applications requiring corrosion resistance or lower friction, stainless steel or ceramic materials may be chosen.
In addition to material quality, heat treatment plays a pivotal role. Through controlled hardening and tempering processes, manufacturers increase the hardness and fatigue resistance of the bearing surfaces. Properly treated steel can resist surface cracks and wear that would otherwise reduce the operational life of deep groove ball bearings.
Precision Manufacturing and Surface Finishing
Manufacturing precision is another fundamental factor. Deep groove ball bearings are designed with tight tolerances to ensure smooth rolling and load distribution. Any deviation in roundness, surface finish, or dimensional accuracy can localized stress, excessive vibration, and premature failure.
Advanced CNC machining and grinding techniques are used to maintain consistent geometries. Surface finishing processes, such as superfinishing or lapping, reduce surface roughness on the raceways and rolling elements, which helps to minimize friction and wear. These practices directly contribute to the long-term reliability of deep groove ball bearings in demanding applications.
Sealing and Shielding Mechanisms
Contamination from dust, moisture, and other foreign particles is a cause of bearing failure. To mitigate this risk, deep groove ball bearings are often equipped with seals or shields. Sealed bearings have contact-type seals that provide better protection but may slightly increase friction. Shielded bearings use non-contact metal shields, which allow for lower friction and moderate protection.
Choosing the right sealing mechanism depends on the application's environment. In high-contamination areas, high-performance rubber seals can prevent ingress of harmful substances, thereby significantly extending the life of the bearing.
Proper lubrication is critical for the smooth operation of deep groove ball bearings. Lubricants reduce metal-to-metal contact, dissipate heat, and prevent corrosion. Grease is the common lubricant used for these bearings due to its ease of application and long-lasting protection.
Key factors include selecting the right type of grease, determining the appropriate quantity, and maintaining scheduled re-lubrication intervals if required. Over-lubrication can cause increased friction and heat, while under-lubrication can metal wear. Manufacturers may pre-fill deep groove ball bearings with grease suited to the expected operating temperature, speed, and load conditions.
Correct Installation and Handling
Even the well-manufactured deep groove ball bearings can fail prematurely if mishandled during installation. Applying excessive force, misaligning the bearing, or contaminating it with dirt or moisture can create internal damage that may not be immediately visible.
Use of proper tools, such as bearing pullers and press-fit devices, ensures the bearing is seated correctly without introducing stress. Installation instructions provided by the manufacturer should always be followed to avoid avoidable defects or performance issues.

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español
