-
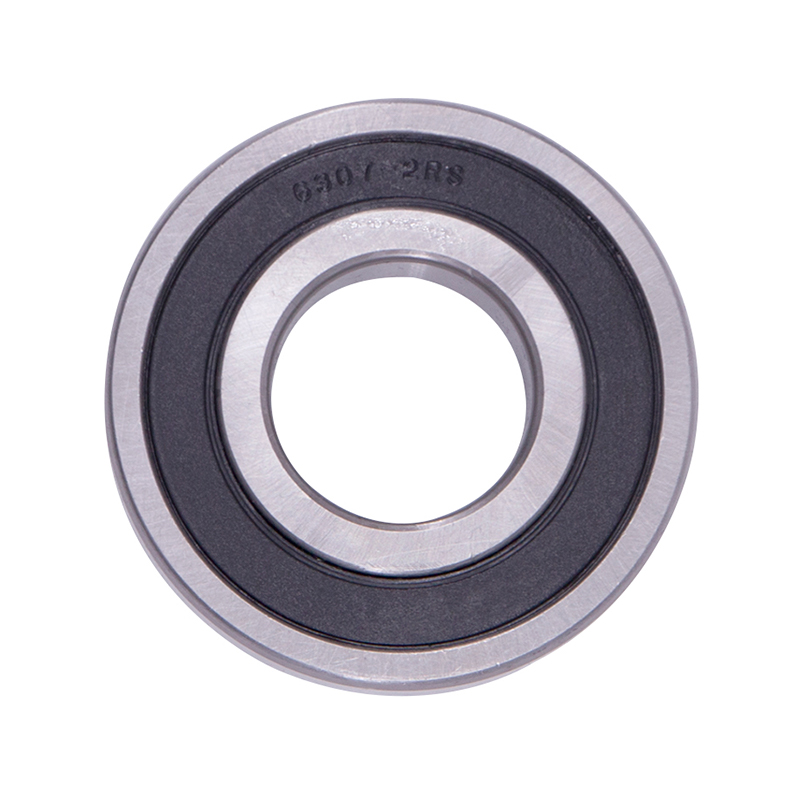 Wheel Hub Bearings
Wheel Hub Bearings -
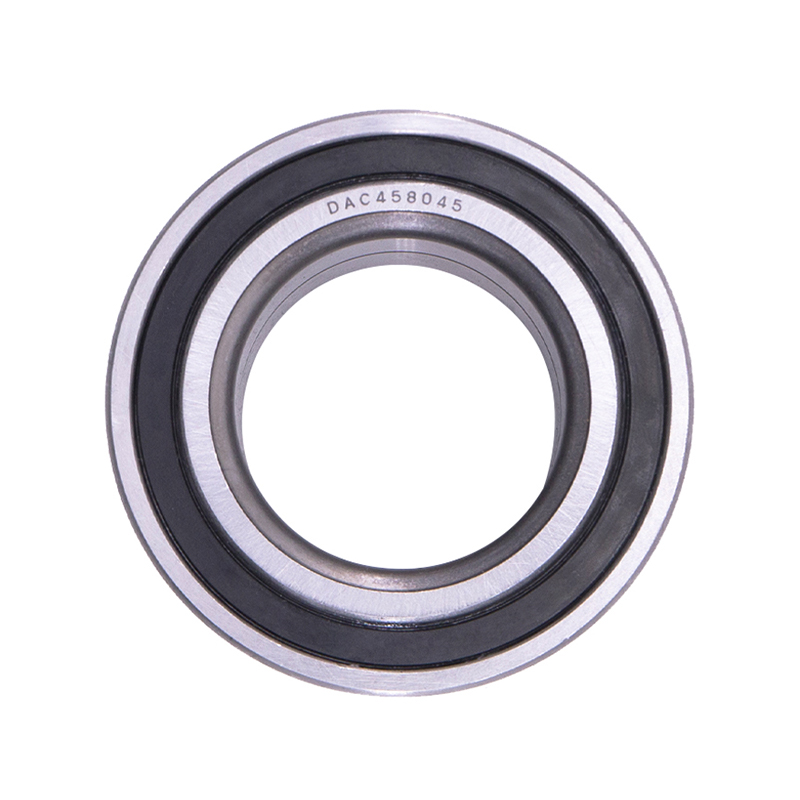 Wheel Hub Bearings
Wheel Hub BearingsDAC387436 DAC458045 Hub Deep Groove Ball Car Wheel Bearing
-
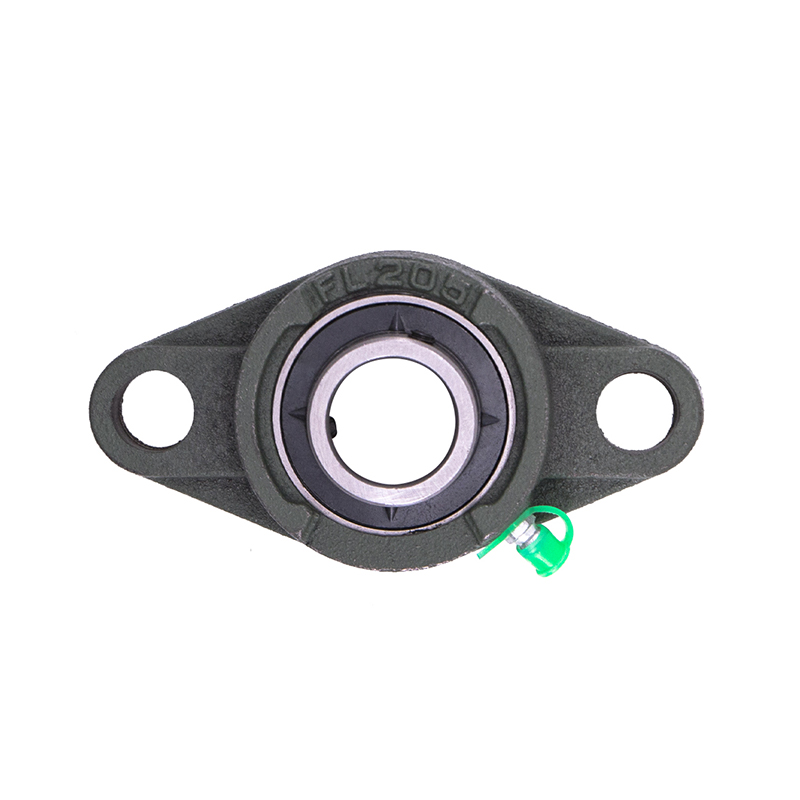 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsFL204 FL205 FL206 Stainless Steel Pillow Block Bearing
-
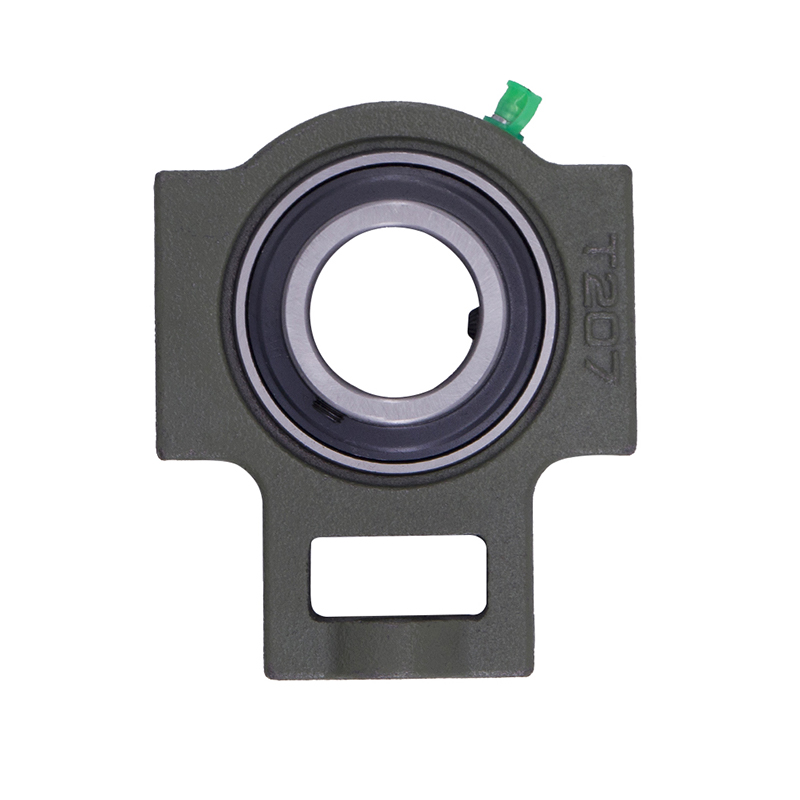 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsT204 T207 UC204 High Speed Insert Pillow Block Bearing
-
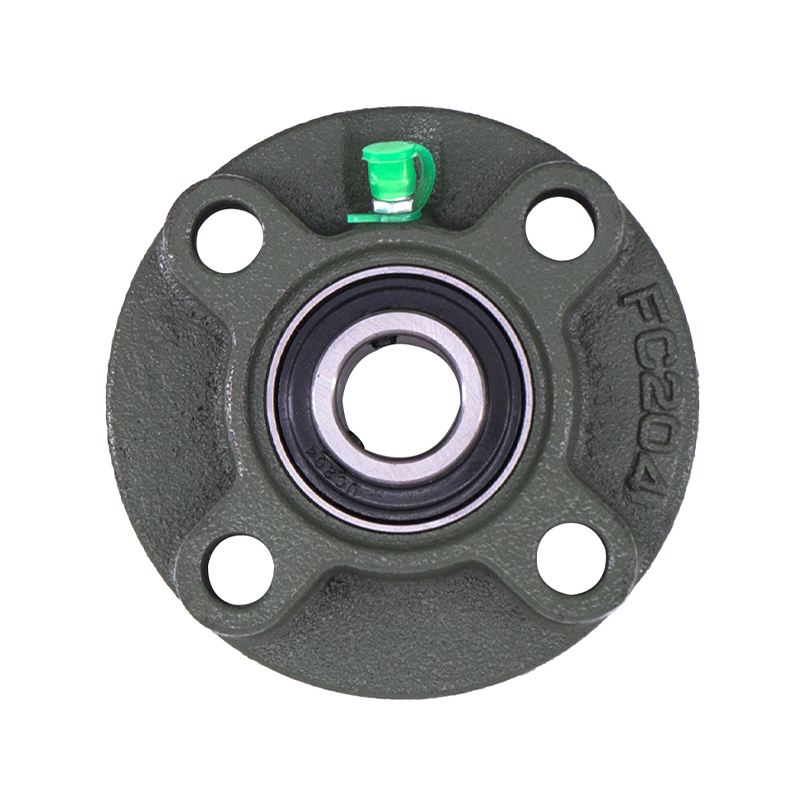 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsFC204 F210 Auto Wheels Bike Pillow Block Bearing
-
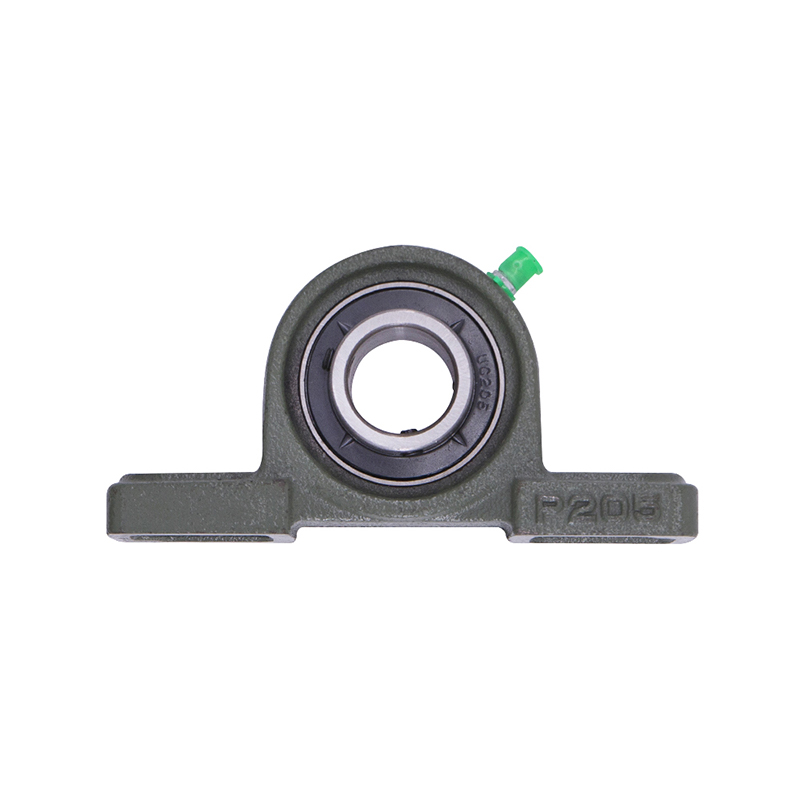 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsP207 206 205 203 High Precision Wheel Pillow Block Bearing
-
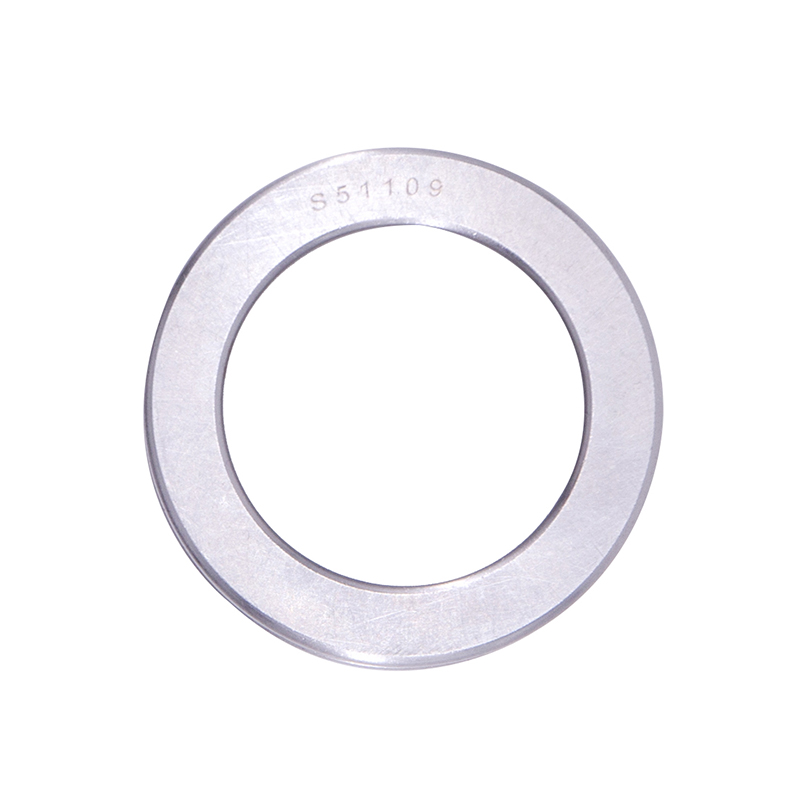 Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust Roller BearingsS51100 S51107 S51109 Car Wheel Plain Thrust Ball Bearing
-
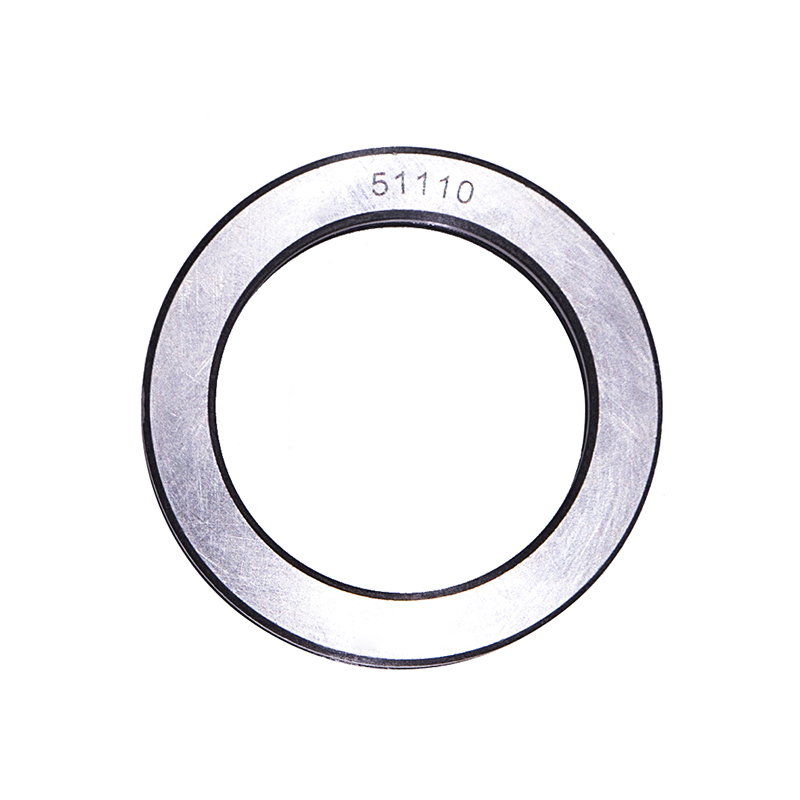 Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust Roller Bearings51110 51107 51104 51206 High Speed Plain Thrust Ball Bearing
Taper Roller Bearing Material Composition: A Key to Performance and Durability
Industry news-The material composition of a taper roller bearing is crucial because it determines the bearing's ability to withstand operational stresses, such as load, temperature fluctuations, and environmental conditions. Let's explore the various materials used in the construction of taper roller bearings.

The common material used for taper roller bearings is high carbon chromium steel. This material is chosen because of its combination of strength, hardness, and wear resistance, making it ideal for applications where the bearing will experience high stresses.
Composition: High carbon chromium steel typically contains 0.95% to 1.05% carbon, 1.3% to 1.65% chromium, and small amounts of other elements such as manganese, silicon, and phosphorus. The high carbon content increases the hardness of the steel, while chromium adds corrosion resistance and improves the material's overall durability.
Role in Taper Roller Bearings: The high carbon content enhances the steel's hardness, which allows the bearing to maintain its shape and function under heavy loads and high-speed operations. Chromium contributes to increased resistance to corrosion and fatigue, which are essential properties for bearings that are exposed to harsh environmental conditions or high temperatures.
Benefits: High carbon chromium steel bearings can operate in a wide range of temperatures, from -20°C to 150°C. They offer wear resistance, ensuring longer service life and lower maintenance costs.
Case-hardening is another technique used to enhance the durability of taper roller bearings. In this process, the outer layer of the bearing material is hardened to provide a wear-resistant surface, while the core remains softer and more resilient to shock loads.
Composition: Case-hardened steel involves the use of low-carbon steel that is treated with heat and carbon to form a hard outer layer. The carbon content is kept low in the core but is increased on the surface to create a hardened case.
Role in Taper Roller Bearings: Case-hardened steel is often used in bearings that will be exposed to moderate load and stress. The hard outer layer resists wear and prevents surface degradation, while the softer core provides the necessary toughness to absorb shock loads.
Benefits: Case-hardened steel improves the bearing's fatigue resistance and impact strength. This makes it particularly useful for applications in which the bearing will face occasional heavy shocks or vibrations, such as in automotive gearboxes.
In addition to high-quality steel, taper roller bearings may also feature a manganese phosphate coating. This coating is often applied to the surface of the bearing components to reduce friction, enhance corrosion resistance, and increase the overall lifespan of the bearing.
Composition: Manganese phosphate coatings are created by a chemical reaction that deposits a layer of manganese phosphate on the steel surface. The coating is typically porous, which allows for the retention of lubricants, reducing friction and wear during operation.
Role in Taper Roller Bearings: Manganese phosphate coatings improve the performance of taper roller bearings by reducing metal-to-metal contact and wear. The porous structure of the coating can also trap lubricants, which helps to maintain the bearing's smooth operation.
Benefits: The manganese phosphate coating increases the bearing's resistance to corrosion, particularly in wet or high-moisture environments. It also helps to extend the service life of the bearing by reducing friction and wear between moving parts.

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español
