-
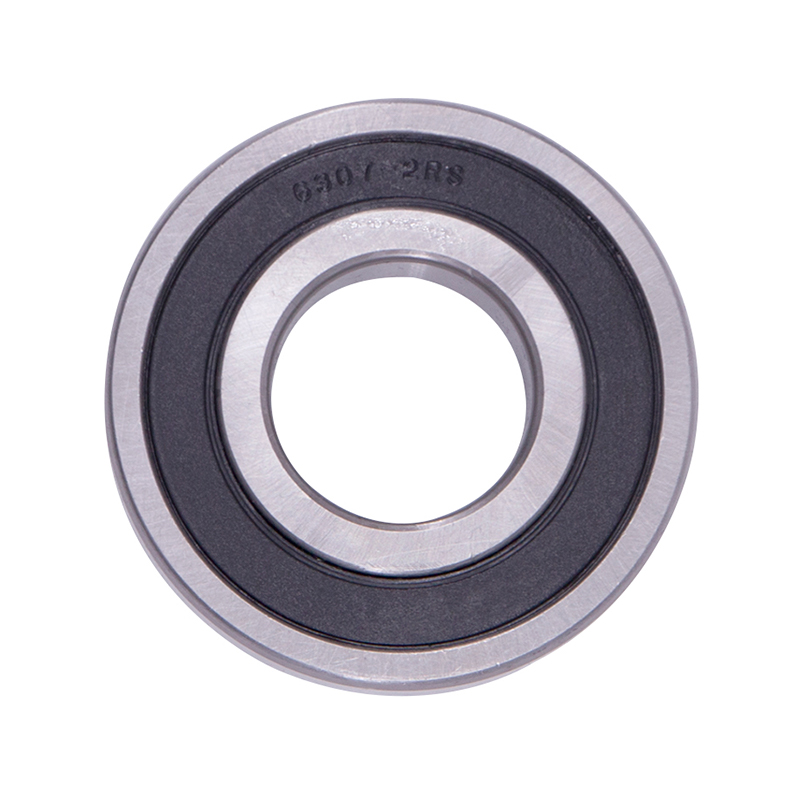 Wheel Hub Bearings
Wheel Hub Bearings -
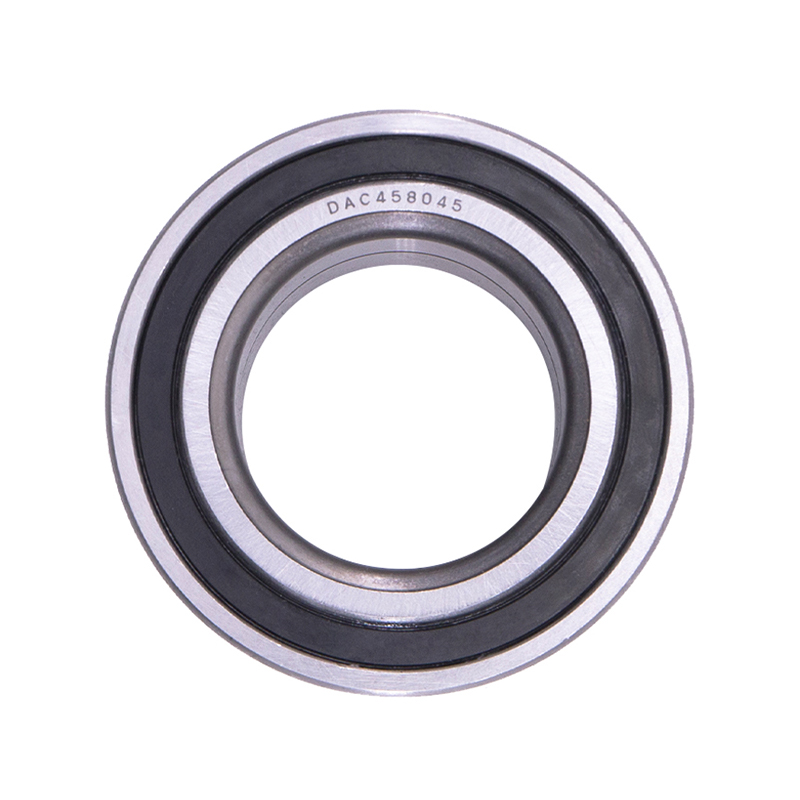 Wheel Hub Bearings
Wheel Hub BearingsDAC387436 DAC458045 Hub Deep Groove Ball Car Wheel Bearing
-
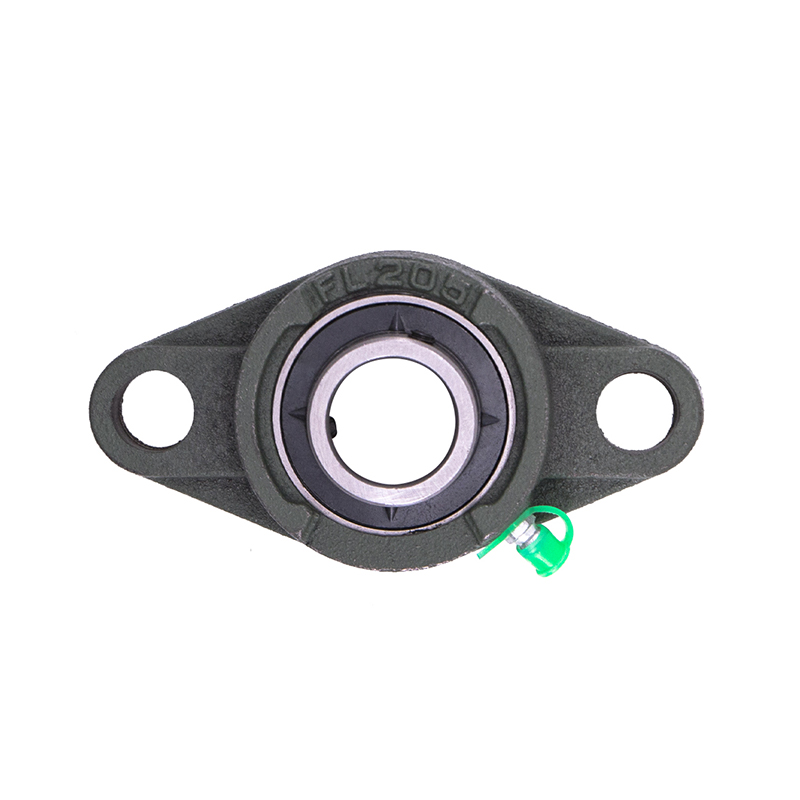 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsFL204 FL205 FL206 Stainless Steel Pillow Block Bearing
-
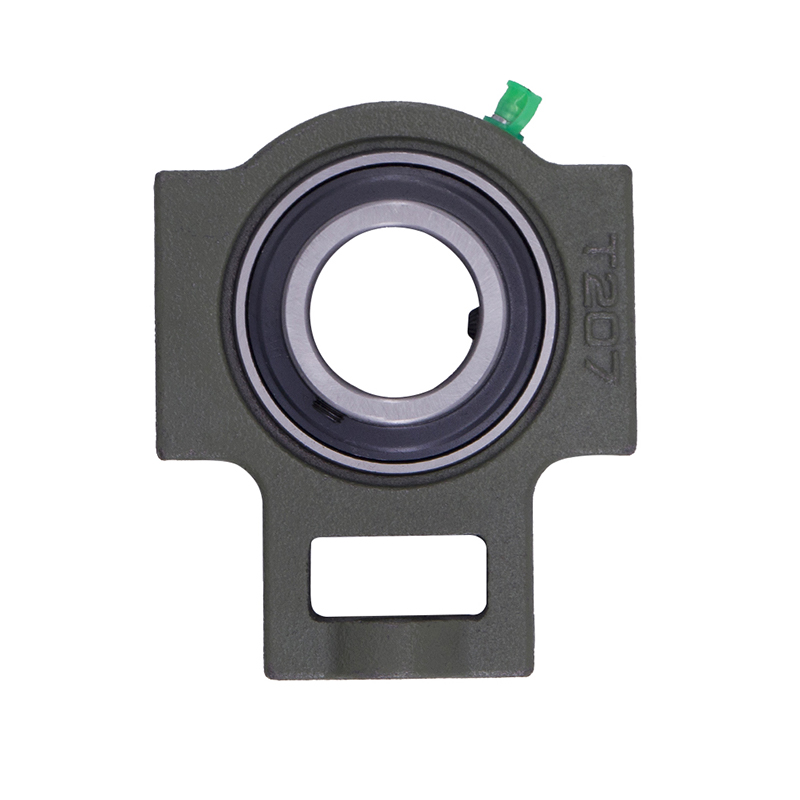 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsT204 T207 UC204 High Speed Insert Pillow Block Bearing
-
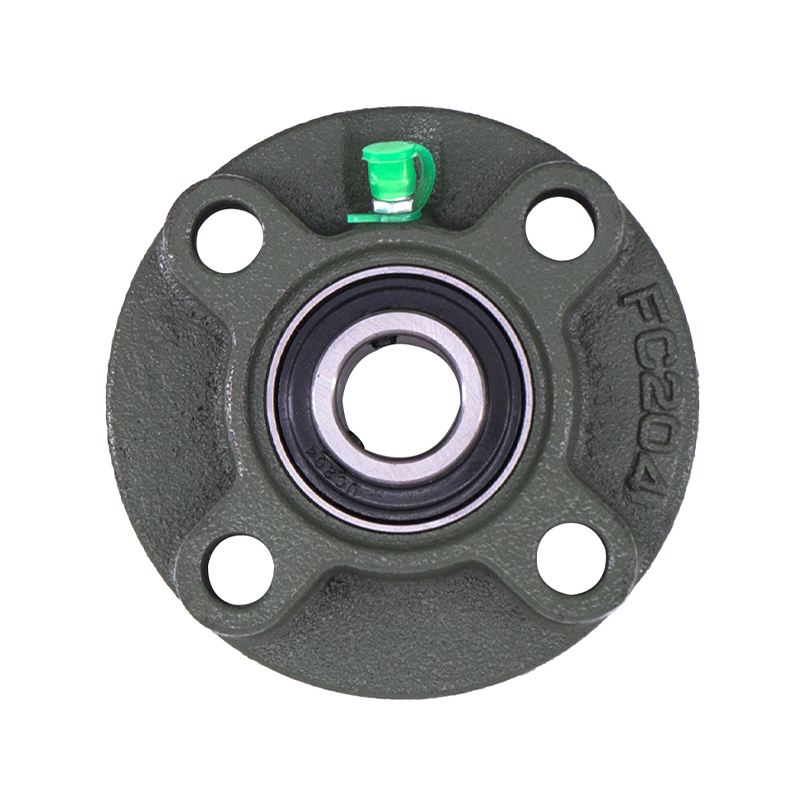 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsFC204 F210 Auto Wheels Bike Pillow Block Bearing
-
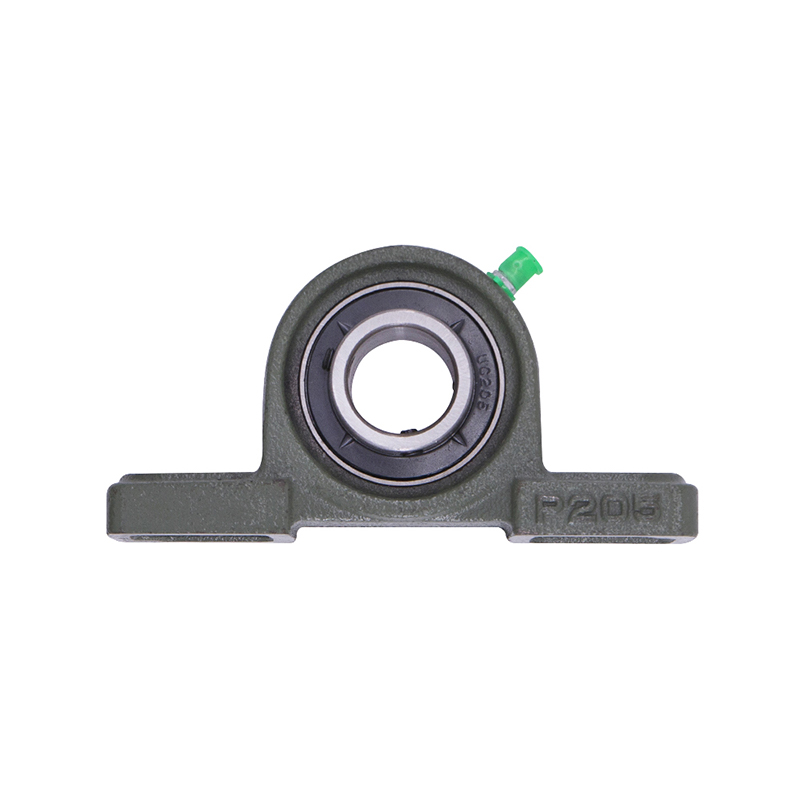 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsP207 206 205 203 High Precision Wheel Pillow Block Bearing
-
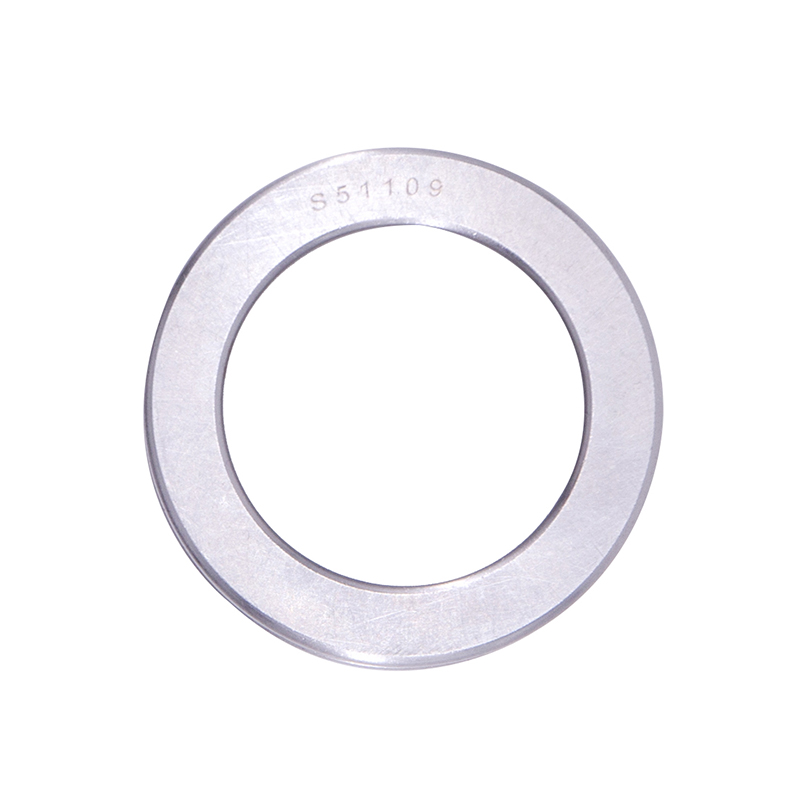 Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust Roller BearingsS51100 S51107 S51109 Car Wheel Plain Thrust Ball Bearing
-
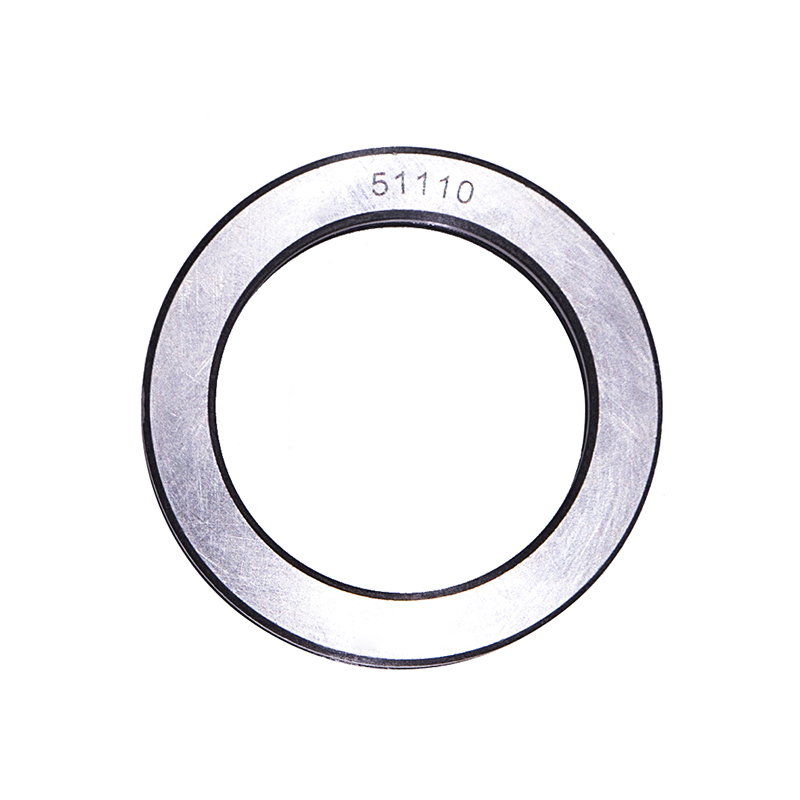 Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust Roller Bearings51110 51107 51104 51206 High Speed Plain Thrust Ball Bearing
Types and Comparisons of Motorcycle Bearings
Industry news-Motorcycle bearings factory play a crucial role in ensuring smooth operation, reducing friction, and supporting rotational components in a motorcycle. They are used in wheels, steering systems, engines, and transmissions, allowing parts to rotate with minimal resistance. Choosing the appropriate type of bearing is essential for performance, durability, and safety.

Importance of Motorcycle Bearings
Bearings are critical in motorcycle design because they ensure smooth movement and reduce wear between rotating components. By friction, bearings help maintain engine efficiency, extend the lifespan of parts, and improve handling and stability. Well-maintained bearings also enhance safety by providing consistent control over wheels, steering, and suspension systems. Selecting the right bearing type can prevent mechanical issues and ensure reliable performance in diverse riding conditions.
Common Types of Motorcycle Bearings
Motorcycle bearings come in various designs, each suited for specific applications. The main types include ball bearings, roller bearings, tapered roller bearings, needle bearings, and ceramic bearings.
1. Ball Bearings
Ball bearings are among the commonly used bearings in motorcycles. They consist of spherical balls held between two rings, allowing rotation with minimal friction.
Characteristics:
Suitable for radial and moderate axial loads.
Provide smooth rotation and reduced friction.
Compact and easy to install.
Commonly used in wheels, engines, and gearboxes.
2. Roller Bearings
Roller bearings use cylindrical or tapered rollers instead of balls. The rollers increase the contact area, which improves load-carrying capacity.
Characteristics:
Handle higher radial loads than ball bearings.
Ideal for applications with heavy rotational forces.
Suitable for transmission shafts, swingarms, and wheel hubs.
Require proper lubrication for long-term performance.
3. Tapered Roller Bearings
Tapered roller bearings have conical rollers arranged between inner and outer rings. They can accommodate both radial and axial loads simultaneously.
Characteristics:
Good for applications with combined loads.
Provide stability for wheels and steering systems.
Often used in front and rear wheel hubs.
Require precise installation for performance.
4. Needle Bearings
Needle bearings are a type of roller bearing with long, thin cylindrical rollers. Their compact design is suitable for applications with limited space.
Characteristics:
High load capacity in small spaces.
Reduce friction in tight assemblies.
Commonly used in rocker arms, swingarms, and gearbox components.
Lightweight and efficient for high-speed applications.
5. Ceramic Bearings
Ceramic bearings feature balls or rollers made from ceramic materials, such as silicon nitride. They are lighter and harder than metal bearings.
Characteristics:
High resistance to heat and corrosion.
Reduced friction and improved rotational speed.
Longer lifespan compared to traditional steel bearings.
Ideal for performance motorcycles and racing applications.
Comparisons of Motorcycle Bearing Types
When comparing different types of motorcycle bearings, several factors are important:
Load Capacity: Roller and tapered roller bearings handle heavier loads, while ball and needle bearings are suitable for moderate loads.
Friction and Speed: Ceramic and ball bearings provide smoother rotation at high speeds, enhancing engine and wheel performance.
Space Requirements: Needle bearings are ideal for compact assemblies, whereas tapered roller bearings require more installation space.
Durability: Ceramic bearings and tapered roller bearings offer higher durability under heavy use and high temperatures.
Maintenance: Proper lubrication and cleaning are essential for all bearing types, with some requiring more frequent attention depending on load and environment.
How to Choose Motorcycle Bearings
Selecting the right bearing depends on the application, load requirements, and riding conditions:
Identify the Application: Determine whether the bearing will be used in wheels, steering, engine, or transmission.
Evaluate Load Requirements: Consider the weight and forces acting on the bearing to choose an appropriate type.
Consider Speed and Performance: High-speed applications benefit from ball or ceramic bearings, while heavy-load areas may require roller or tapered bearings.
Assess Space Limitations: Choose needle or compact ball bearings for confined areas with limited clearance.
Review Maintenance Needs: Bearings in high-stress or exposed environments may need more frequent lubrication and inspection.
Applications of Motorcycle Bearings
Motorcycle bearings are versatile and are used in:
Wheels: Supporting smooth rotation and handling.
Steering Systems: Ensuring stable control and minimal friction.
Engines and Gearboxes: Facilitating efficient rotation and load distribution.
Suspension Systems: Supporting swingarms and other moving parts.

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español
