-
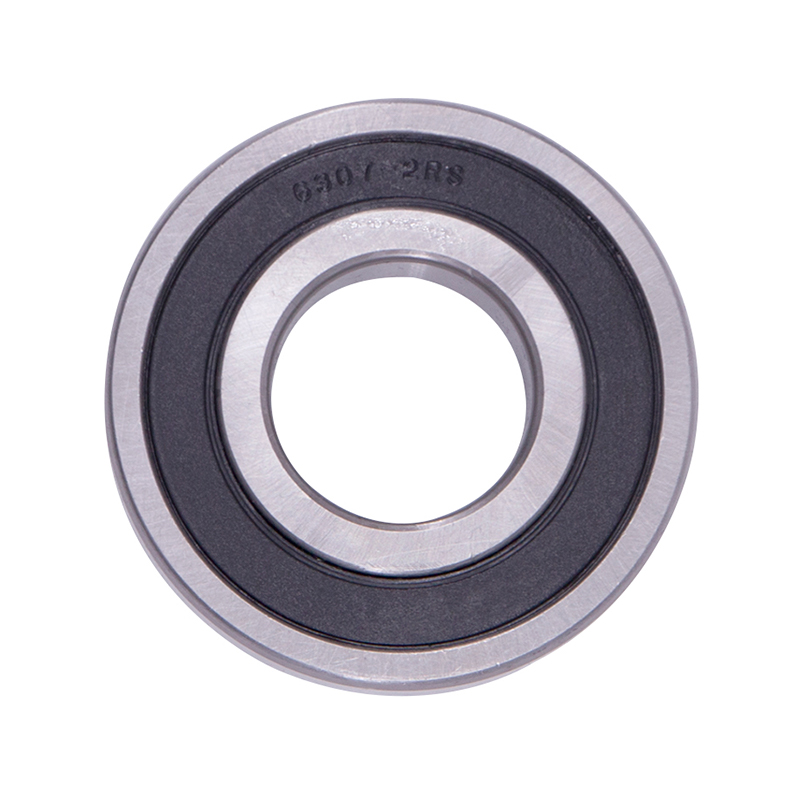 Wheel Hub Bearings
Wheel Hub Bearings -
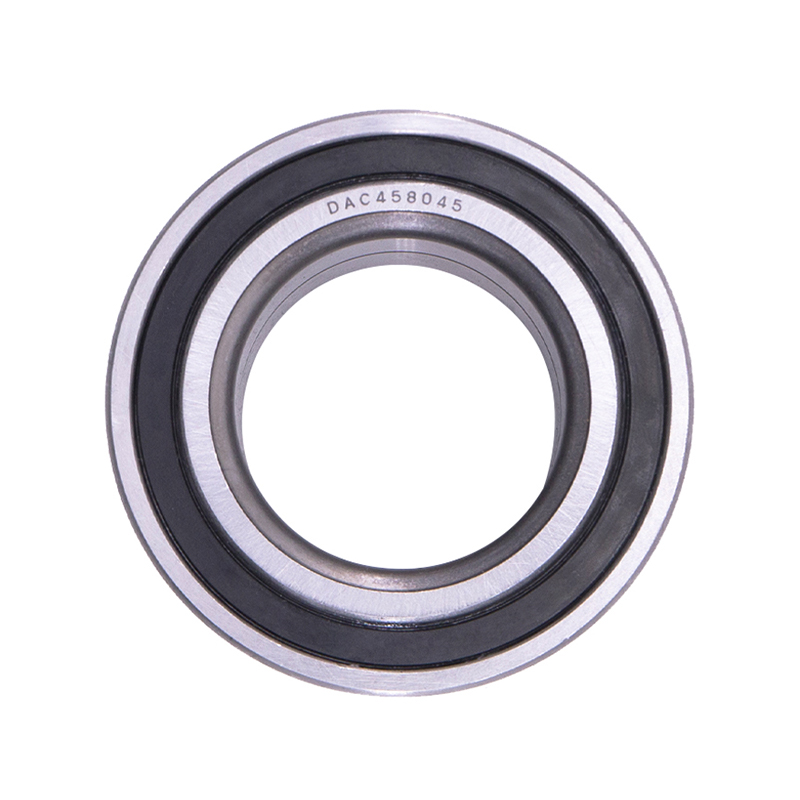 Wheel Hub Bearings
Wheel Hub BearingsDAC387436 DAC458045 Hub Deep Groove Ball Car Wheel Bearing
-
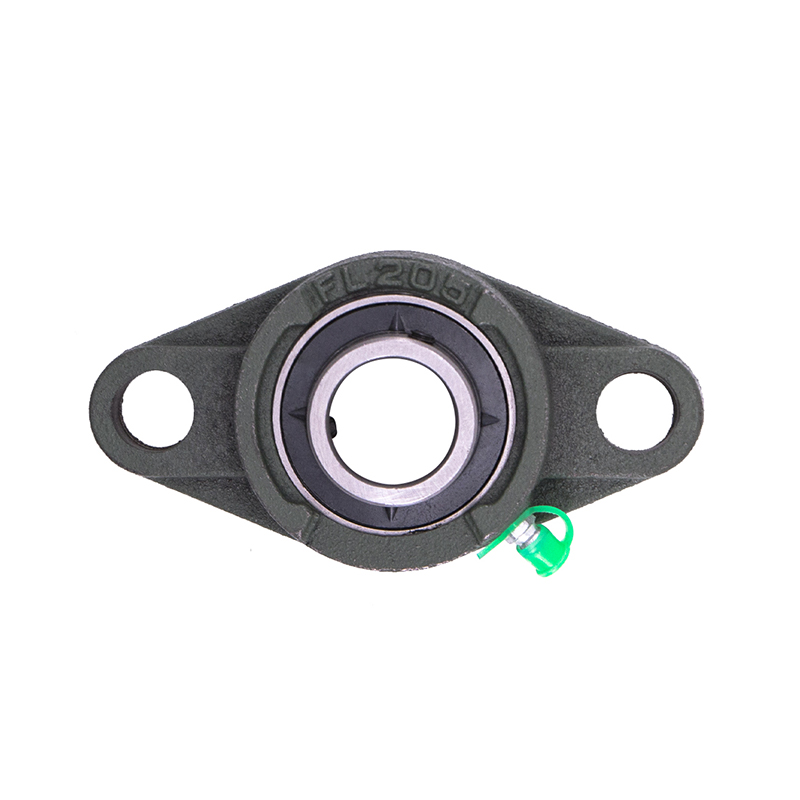 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsFL204 FL205 FL206 Stainless Steel Pillow Block Bearing
-
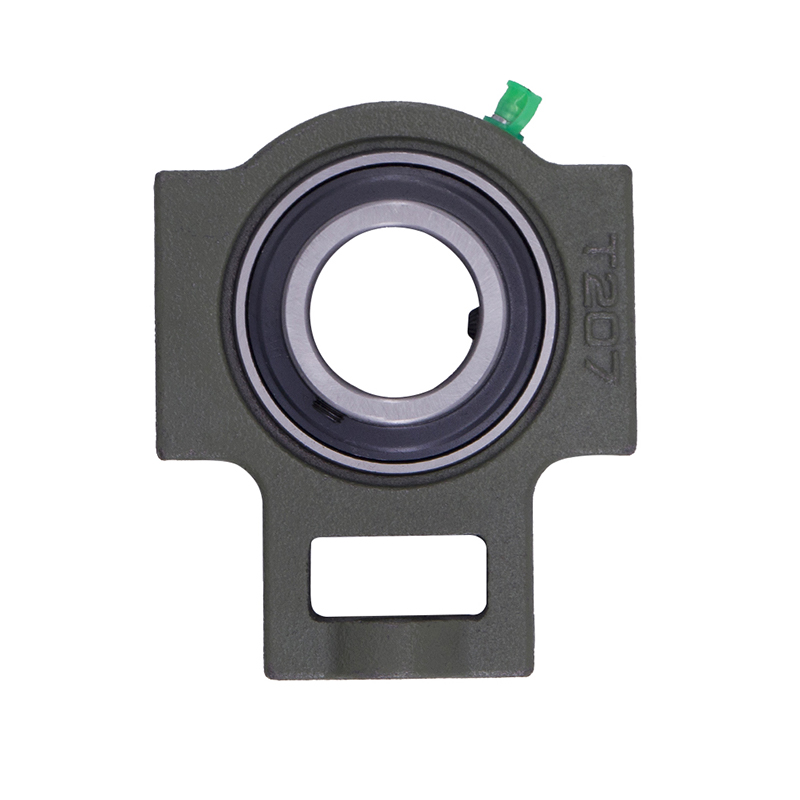 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsT204 T207 UC204 High Speed Insert Pillow Block Bearing
-
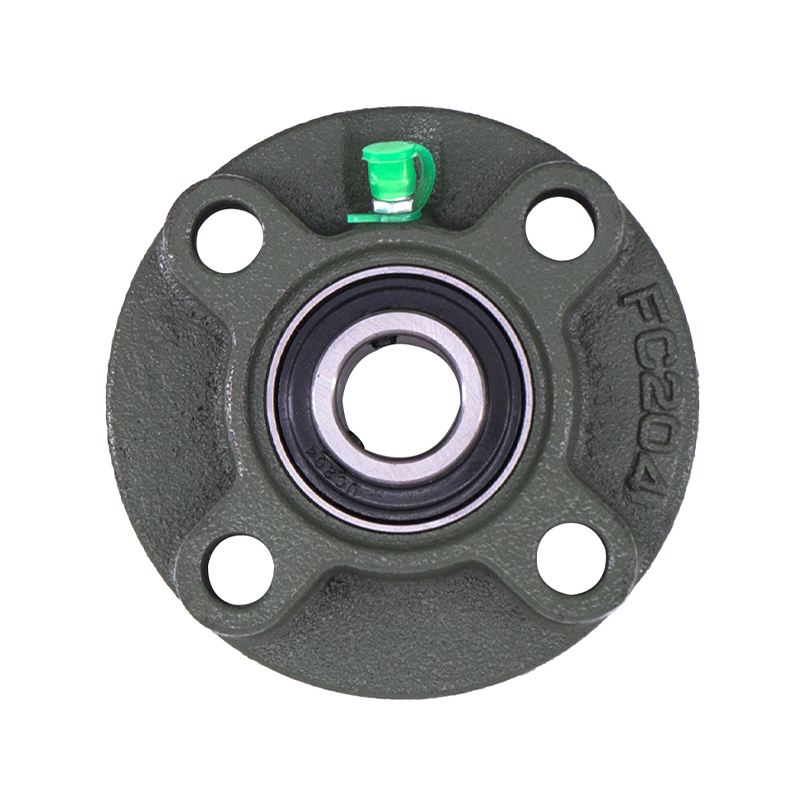 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsFC204 F210 Auto Wheels Bike Pillow Block Bearing
-
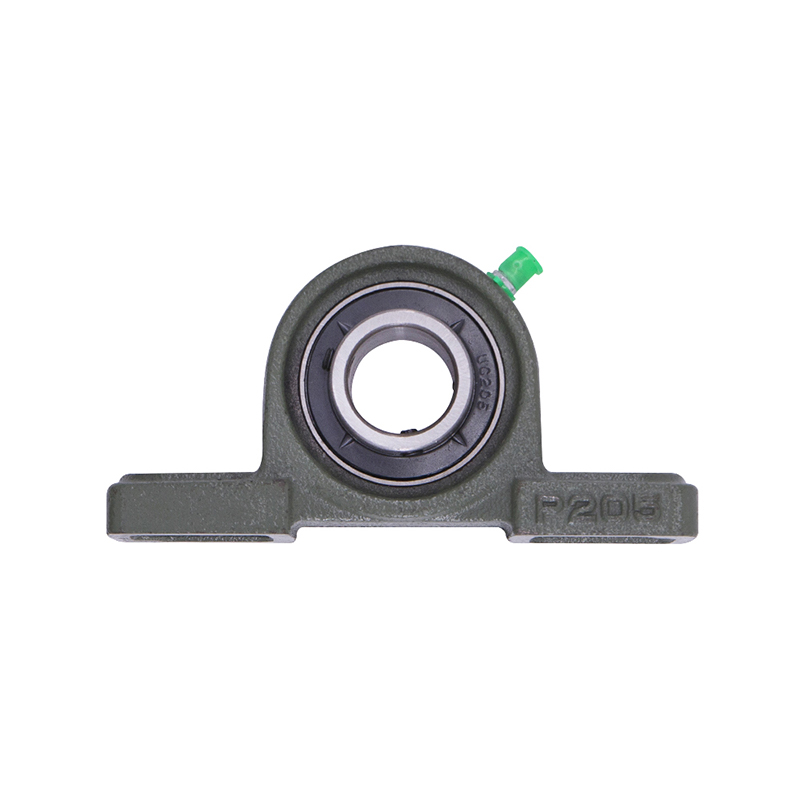 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsP207 206 205 203 High Precision Wheel Pillow Block Bearing
-
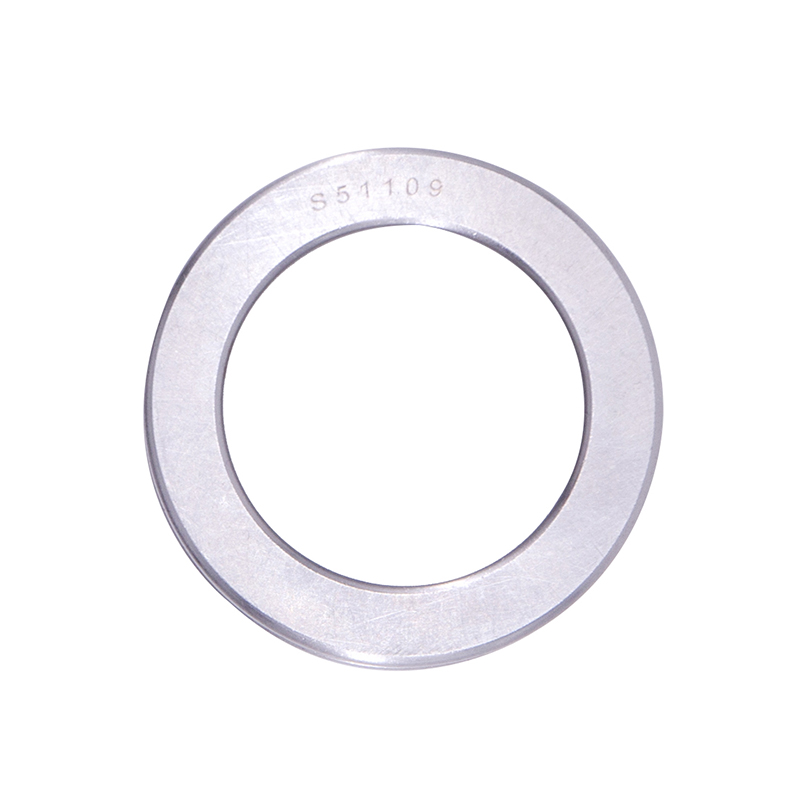 Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust Roller BearingsS51100 S51107 S51109 Car Wheel Plain Thrust Ball Bearing
-
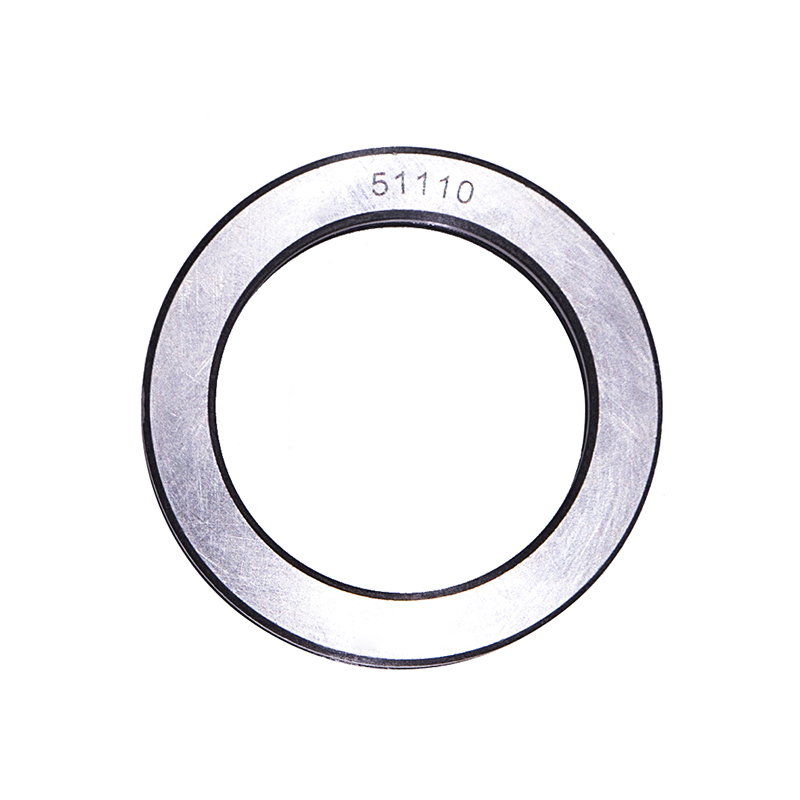 Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust Roller Bearings51110 51107 51104 51206 High Speed Plain Thrust Ball Bearing
How Reliable Are Double Row Angular Contact Ball Bearings?
Industry news-Reliability is a primary public concern because bearing failure can bring about equipment downtime, safety risks, and high maintenance costs. Double row angular contact ball bearings are generally designed to offer stable performance due to their internal structure, which is similar to two single-row angular contact bearings arranged back-to-back or face-to-face.

From an engineering perspective, their reliability depends on correct load distribution across both rows of balls. When properly installed and loaded within rated limits, these bearings can handle axial loads in both directions and maintain good rotational accuracy. This makes them suitable for applications where shaft positioning is critical.
However, reliability is not guaranteed by design alone. Factors such as lubrication quality, contamination control, alignment accuracy, and operating temperature strongly influence service life. Public concern often arises when bearings fail prematurely, but in many cases, the root cause is improper application rather than inherent design weakness. With correct selection and maintenance, double row angular contact ball bearings are considered dependable components in long-term operation.
Are These Bearings Suitable for High-Speed Applications?
High-speed capability is another topic of public interest, particularly as machinery becomes more compact and operates at higher rotational speeds. Double row angular contact ball bearings can operate at relatively high speeds, but their limits are influenced by internal geometry and lubrication conditions.
Compared with single-row angular contact bearings, double row designs generally have slightly lower speed ratings. This is due to increased internal friction caused by the additional row of rolling elements and more complex contact angles. As a result, heat generation becomes a key consideration at elevated speeds.
To address this concern, manufacturers optimize ball precision, cage design, and surface finishes to reduce friction. In practical use, these bearings perform well in moderate to high-speed applications where both axial stiffness and load capacity are required. However, for high-speed systems with minimal axial load, alternative bearing types may be more suitable.
What About Installation and Maintenance Complexity?
Installation and maintenance are frequently discussed by equipment operators and maintenance teams, as errors in these areas can significantly shorten bearing life. Double row angular contact ball bearings are often perceived as more complex than standard deep groove ball bearings.
Key points of public concern include:
Installation accuracy: Proper shaft and housing tolerances are essential to prevent excessive preload or internal clearance issues.
Alignment requirements: Misalignment can increase internal stress and accelerate wear.
Lubrication management: Correct grease or oil selection and replenishment intervals are necessary to control friction and heat.
Despite these concerns, double row angular contact ball bearings are typically supplied as matched, pre-assembled units. This reduces the need for complex adjustment during installation compared with paired single-row bearings. When clear installation guidelines are followed, maintenance requirements are predictable and manageable.
How Do Cost and Sustainability Affect Bearing Selection?
Cost and sustainability have become increasingly important public topics, especially in industries aiming to balance performance with responsible resource use. Double row angular contact ball bearings often have higher initial costs than simpler bearing types due to their more complex design and manufacturing process.
However, public concern is shifting toward total cost of ownership rather than purchase price alone. These bearings can replace two separate single-row bearings in some applications, simplifying assembly and reducing the number of components. This can lower installation time, reduce alignment errors, and improve overall system reliability.
From a sustainability standpoint, longer service life and reduced failure rates contribute to lower material consumption and less frequent replacement. Modern bearing manufacturing also emphasizes efficient material use, improved heat treatment processes, and cleaner production methods.
While bearings themselves are mechanical components, their role in energy-efficient machinery indirectly supports sustainability goals. Smooth rotation, reduced friction, and stable load handling all help lower energy losses in mechanical systems.

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español
