-
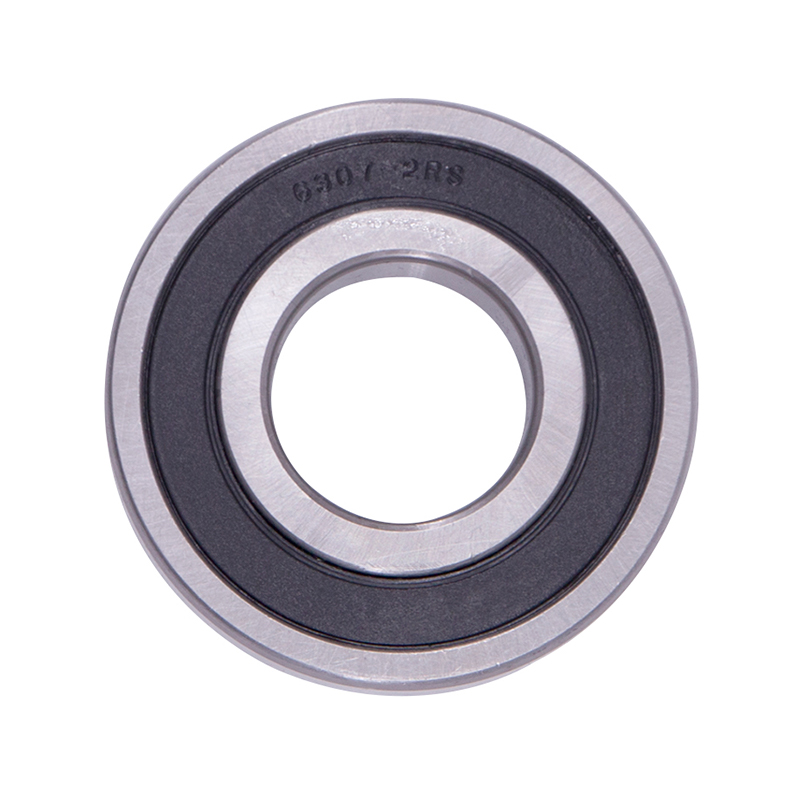 Wheel Hub Bearings
Wheel Hub Bearings -
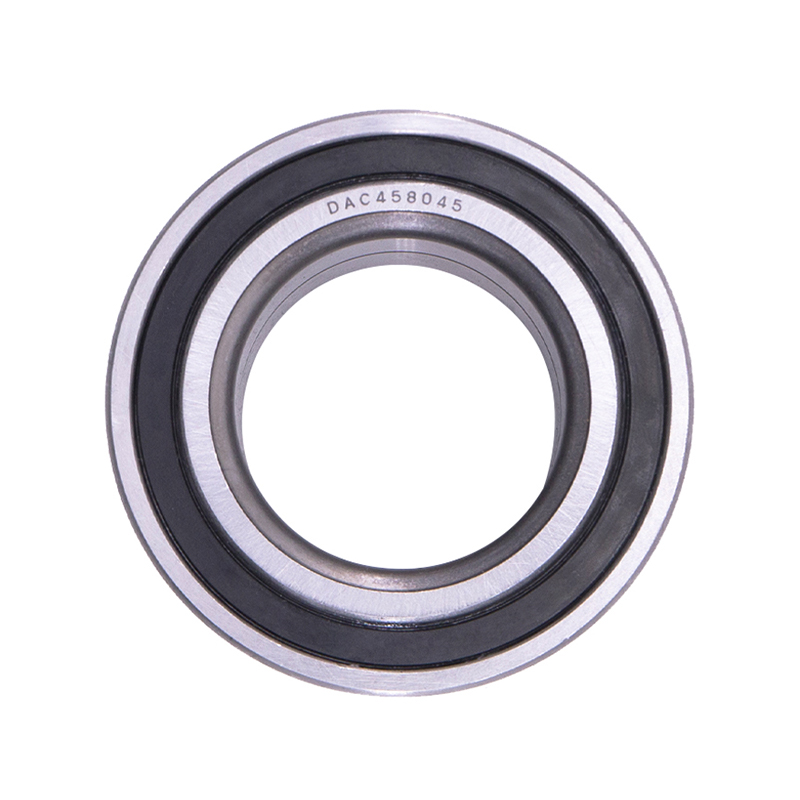 Wheel Hub Bearings
Wheel Hub BearingsDAC387436 DAC458045 Hub Deep Groove Ball Car Wheel Bearing
-
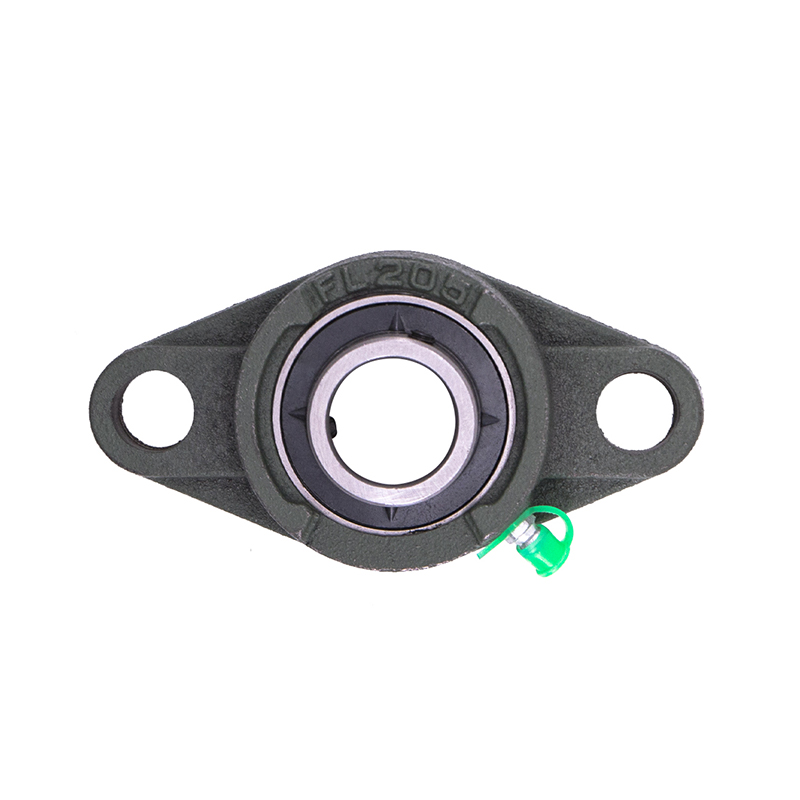 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsFL204 FL205 FL206 Stainless Steel Pillow Block Bearing
-
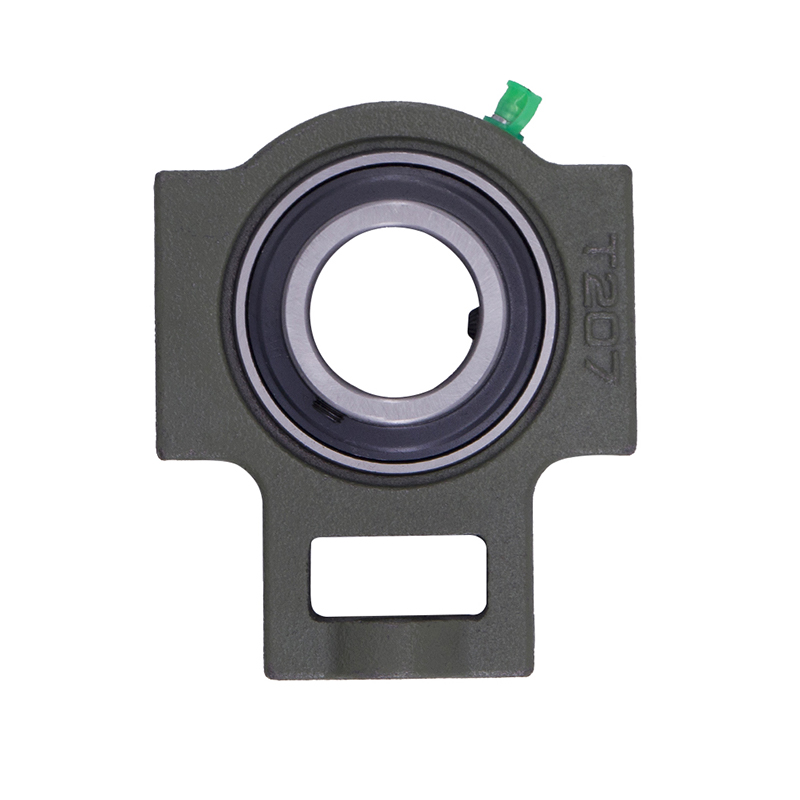 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsT204 T207 UC204 High Speed Insert Pillow Block Bearing
-
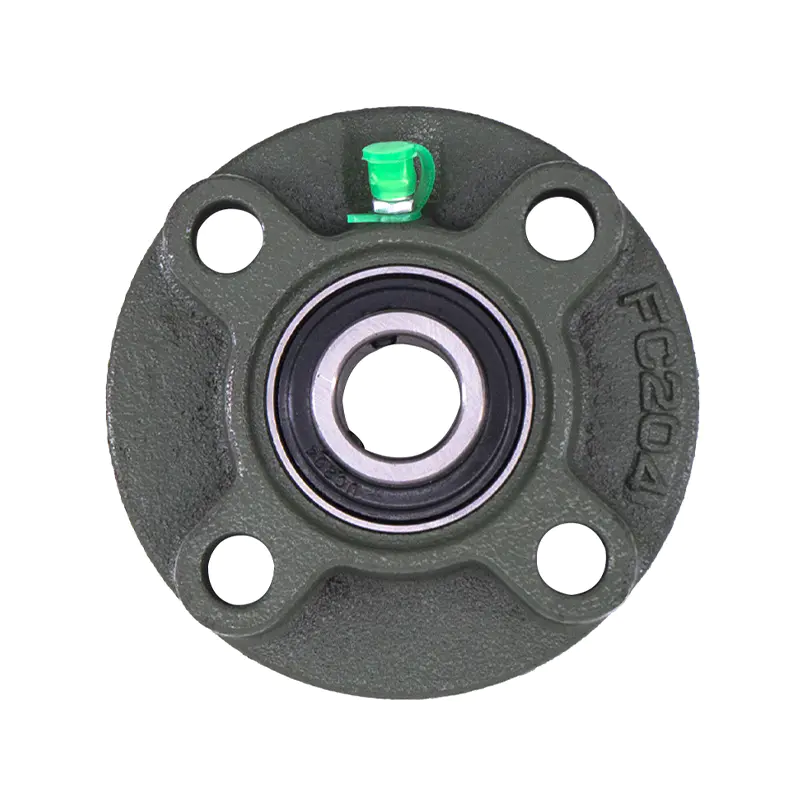
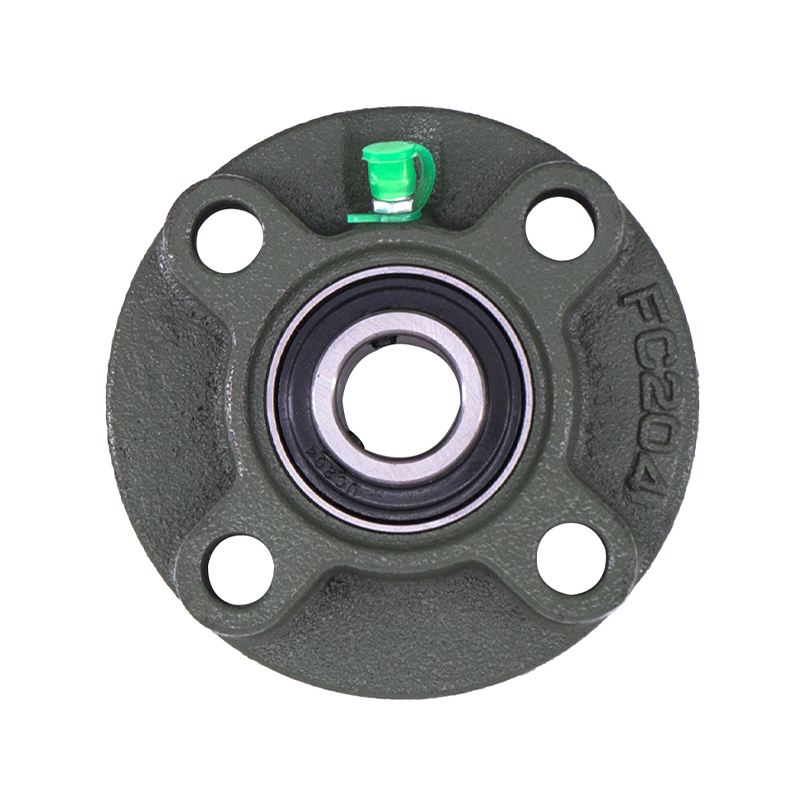 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsFC204 F210 Auto Wheels Bike Pillow Block Bearing
-
 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsP207 206 205 203 High Precision Wheel Pillow Block Bearing
-
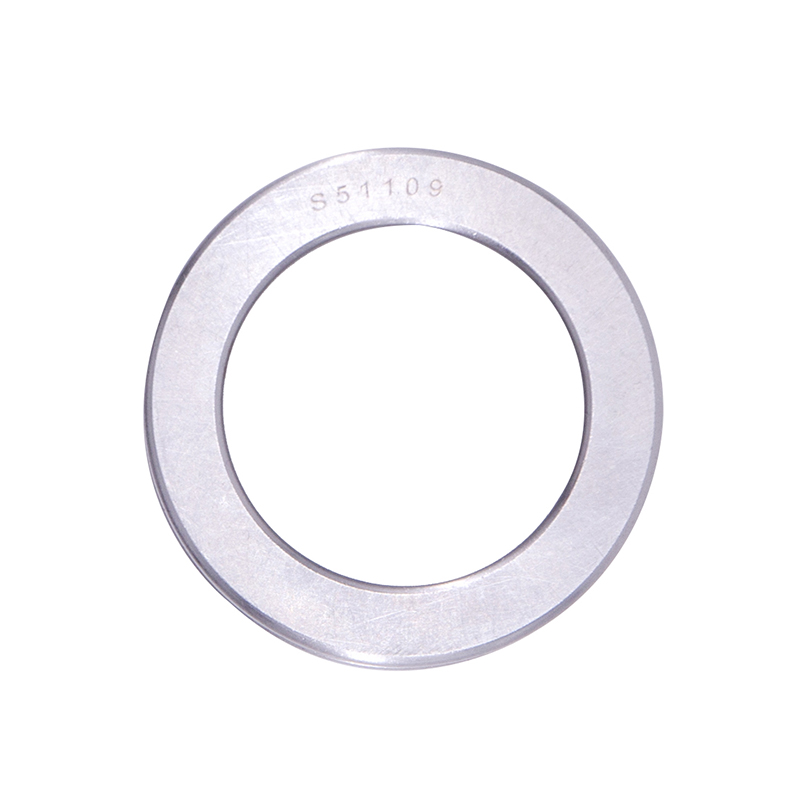 Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust Roller BearingsS51100 S51107 S51109 Car Wheel Plain Thrust Ball Bearing
-
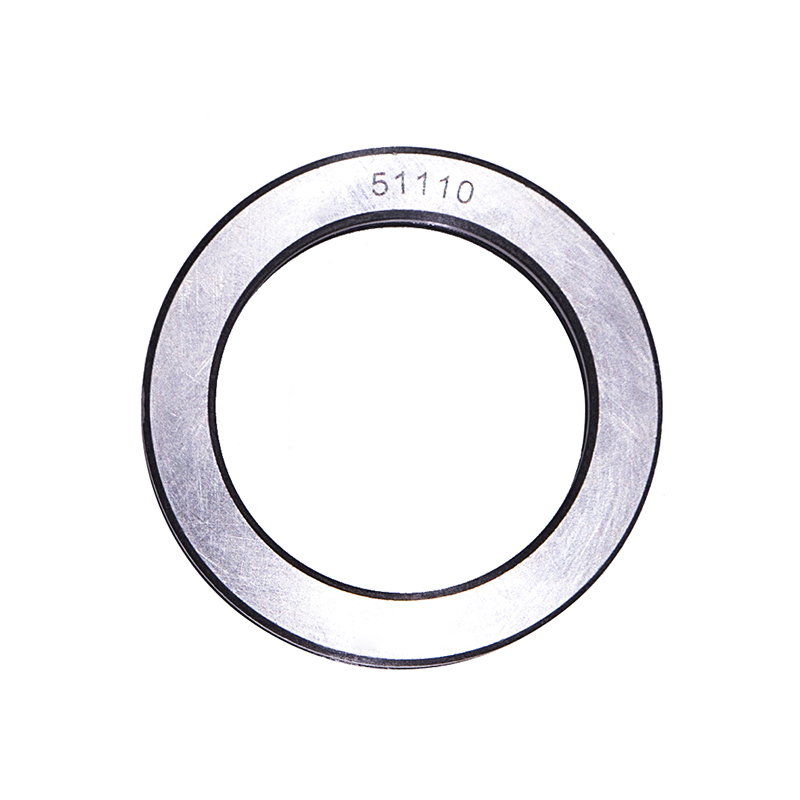 Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust Roller Bearings51110 51107 51104 51206 High Speed Plain Thrust Ball Bearing
Selection of Taper Roller Bearing: A Comprehensive Guide
Industry news-When it comes to machinery and equipment that involve rotational motion, bearings play an essential role in reducing friction and wear. Among the various types of bearings, taper roller bearings are widely used due to their unique ability to handle both radial and axial loads simultaneously. From automotive applications to industrial machinery, taper roller bearings are a vital component in ensuring smooth and efficient operations.

These bearings are typically used in applications where large radial loads, combined with axial loads, need to be supported. The key characteristics of taper roller bearings include:
Axial Load Capacity: Taper roller bearings are capable of handling heavy axial loads.
Radial Load Capacity: They can also accommodate substantial radial loads, making them suitable for high-stress environments.
Angular Contact: The rollers are oriented at an angle, which makes them suitable for applications where both axial and radial forces are present.
There are several different types of taper roller bearings, and selecting the right one depends on the application's requirements. These include:
The common type of taper roller bearing, the single-row version, consists of a single row of tapered rollers. It is designed to handle a combination of radial and axial loads, making it ideal for applications like automotive wheel hubs, construction equipment, and industrial machinery.
Double-row taper roller bearings consist of two rows of rollers, which allows them to handle heavier loads than their single-row counterparts. They are typically used in applications where space constraints limit the use of larger bearings or in applications that require higher load capacity, such as gearboxes, machine tool spindles, and heavy-duty motors.
These bearings are used in applications that demand high load capacity in both radial and axial directions, such as in steel rolling mills or large mining equipment. The four-row configuration provides enhanced load distribution and can handle stresses, but they are typically larger and more expensive.
In separate type taper roller bearings, the inner and outer raceways, as well as the rollers, are made as separate components. This design allows for easier assembly and disassembly, making it suitable for applications where maintenance is a priority, such as in automotive axles or conveyor systems.
Selecting the right taper roller bearing requires careful consideration of several key factors. Here are the main aspects you should keep in mind:
The primary function of taper roller bearings is to handle both radial and axial loads. When selecting a bearing, it is essential to evaluate the magnitude and direction of the loads that will be acting on the bearing in your application. You need to consider the following:
Radial Load: The load that is applied perpendicular to the axis of the shaft. This is typically the weight or force that the bearing will support in a rotating system.
Axial Load: The force that is applied parallel to the axis of the shaft. This is especially relevant in applications where the bearing must resist forces that act along the shaft, such as in automotive applications.
The combination of radial and axial load helps determine the type and size of the taper roller bearing required.
The operating speed and rotational requirements of your application are crucial in determining which taper roller bearing is suitable. If the bearing will be subjected to high-speed rotation, it is important to ensure that the bearing is designed for such conditions. High-speed applications require bearings with low friction, good lubrication, and heat dissipation.
For instance, if the bearing is intended for use in an electric motor, the load-bearing capacity and speed of the motor must be carefully matched with the bearing's specifications.
Taper roller bearings come in a variety of sizes, and selecting the right size is crucial for the bearing's performance. The size is determined by the diameter of the inner and outer raceways, as well as the length and width of the roller. A bearing that is too small for the application will not have the necessary load capacity, while a bearing that is too large may take up unnecessary space and incur higher costs.
To choose the appropriate size, refer to the bearing manufacturer's sizing charts, which provide details on the correct bearing dimensions based on load, speed, and application type.

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español
