-
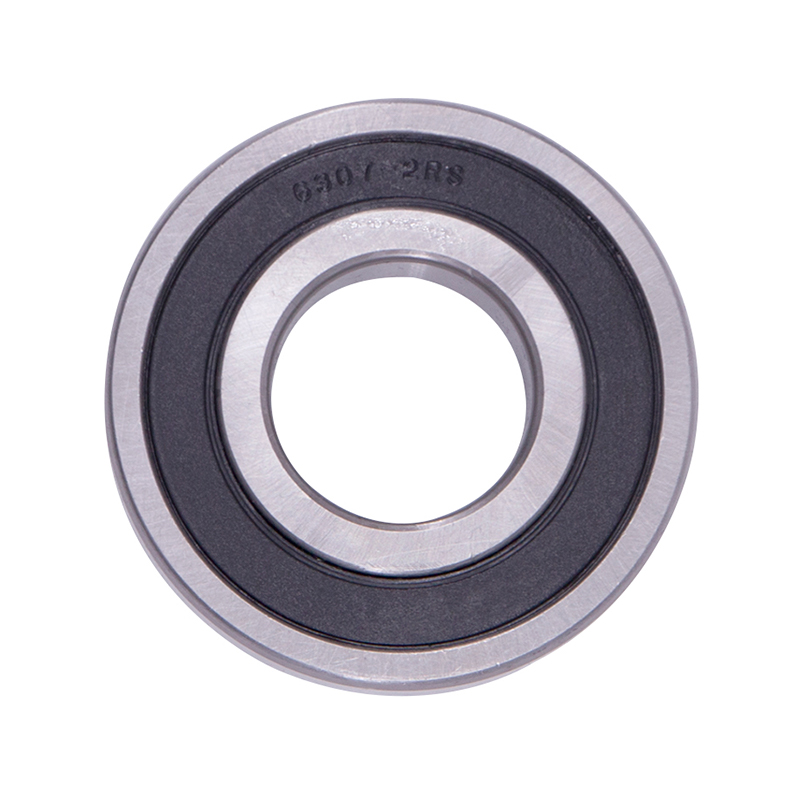 Wheel Hub Bearings
Wheel Hub Bearings -
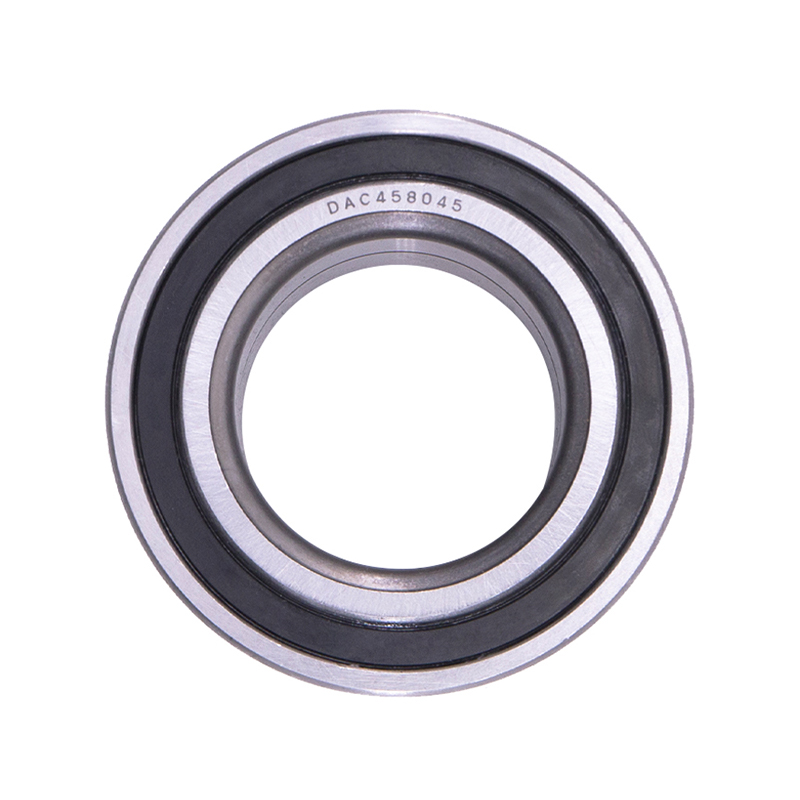 Wheel Hub Bearings
Wheel Hub BearingsDAC387436 DAC458045 Hub Deep Groove Ball Car Wheel Bearing
-
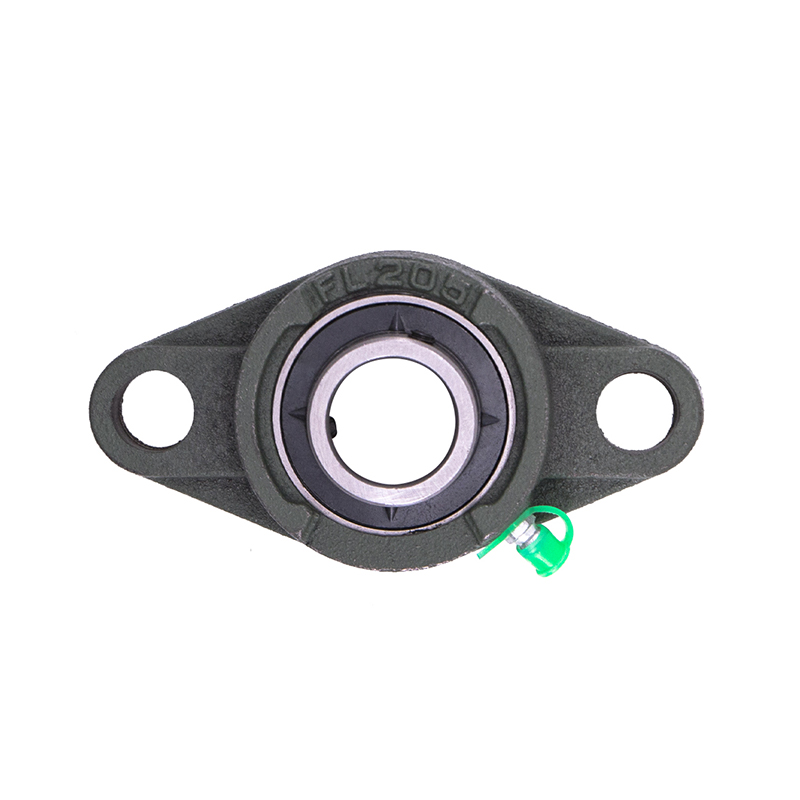 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsFL204 FL205 FL206 Stainless Steel Pillow Block Bearing
-
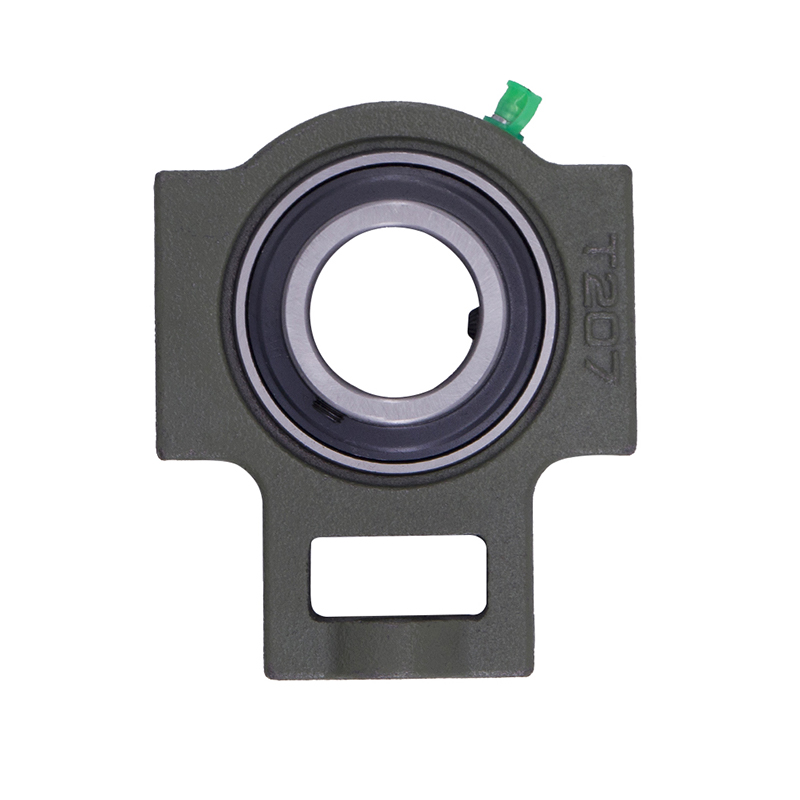 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsT204 T207 UC204 High Speed Insert Pillow Block Bearing
-
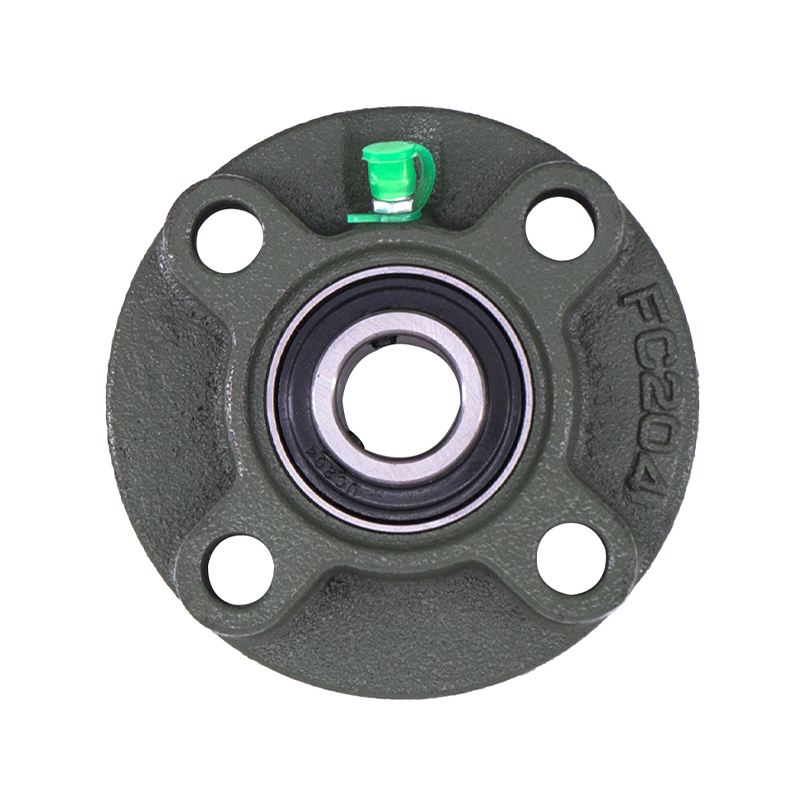 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsFC204 F210 Auto Wheels Bike Pillow Block Bearing
-
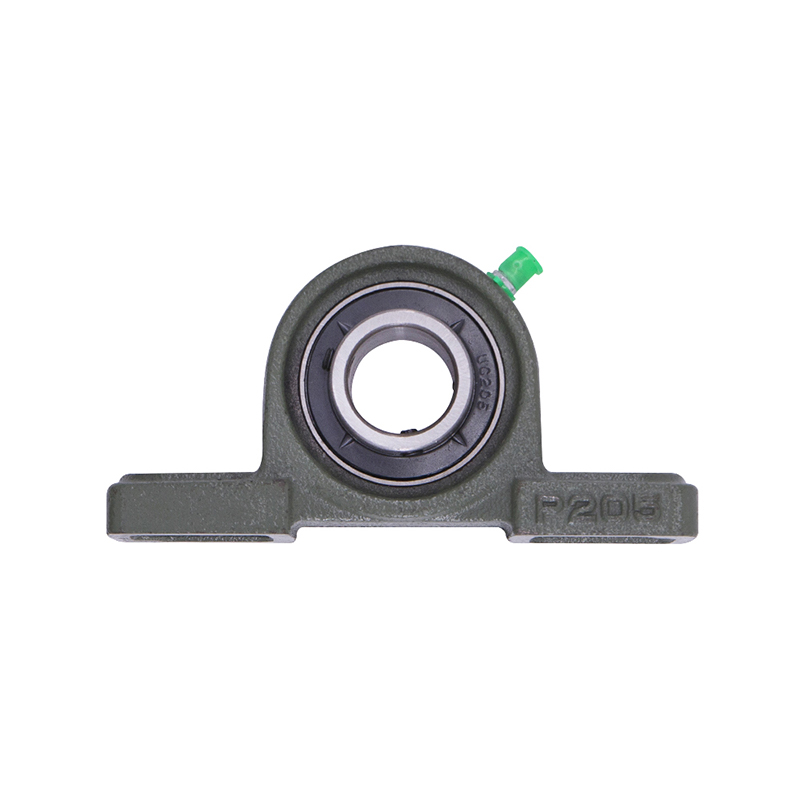 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsP207 206 205 203 High Precision Wheel Pillow Block Bearing
-
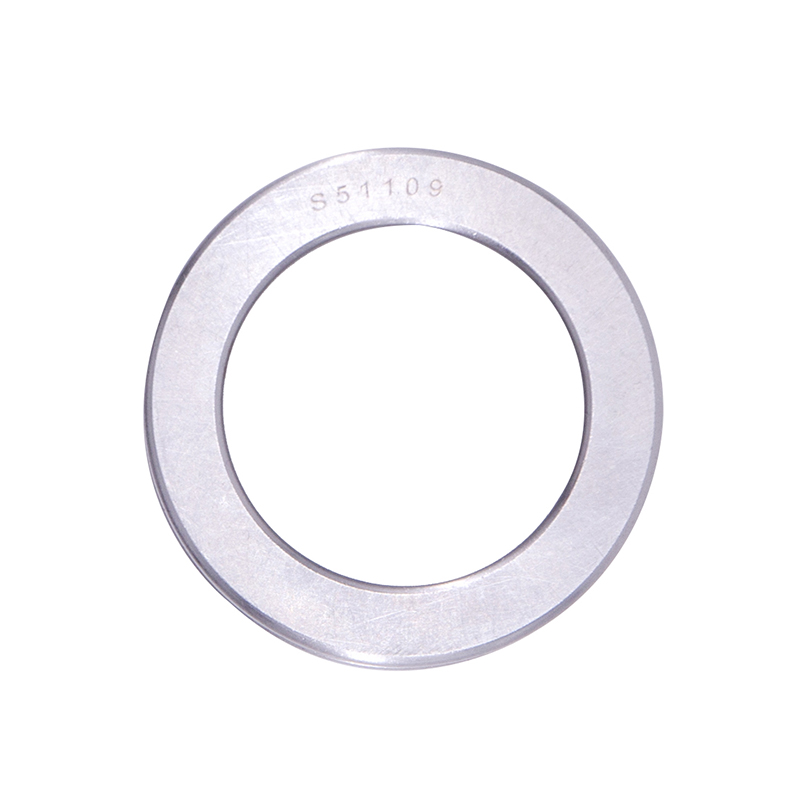 Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust Roller BearingsS51100 S51107 S51109 Car Wheel Plain Thrust Ball Bearing
-
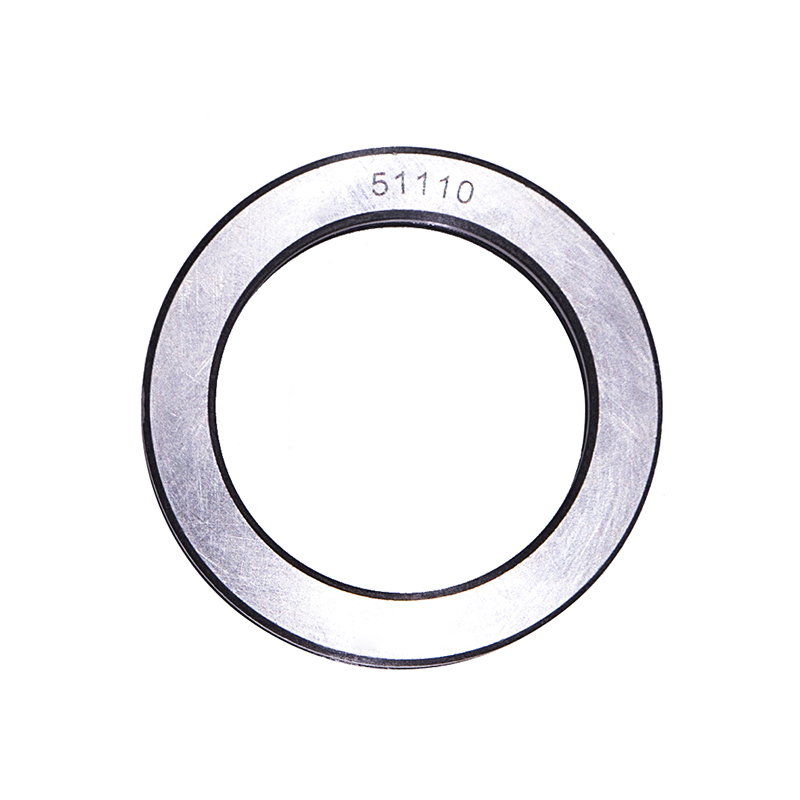 Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust Roller Bearings51110 51107 51104 51206 High Speed Plain Thrust Ball Bearing
What Does a Motorcycle Bearing Include?
Industry news-Motorcycles are complex machines that consist of various components working together to deliver smooth performance and reliability. Among these components, bearings play a crucial role in ensuring that the moving parts of a motorcycle function smoothly, with minimal friction and wear. The term "motorcycle bearing" encompasses a wide range of bearings, each designed to serve a specific purpose within the motorcycle's mechanical system.

Motorcycles typically use several different types of bearings, each chosen for its specific characteristics, such as load capacity, durability, and suitability for a particular application. The following are the common types of bearings found in motorcycles:
Wheel bearings are among the critical components in any motorcycle, as they enable the wheels to rotate smoothly with minimal friction. These bearings are typically located within the wheel hubs and help support the load of the motorcycle while it is in motion. Wheel bearings are generally exposed to high radial loads and are often subjected to significant stresses, especially during cornering or braking.
Ball Bearings: Many motorcycles use ball bearings in the wheels due to their ability to handle radial loads. These are the common type of bearing used in the front and rear wheels.
Tapered Roller Bearings: Some high-performance motorcycles use tapered roller bearings in the wheel hubs. These bearings are designed to handle both radial and axial loads, making them ideal for situations that involve heavy cornering or high-speed riding.
The steering head bearings are located at the point where the motorcycle's front fork is connected to the frame. These bearings are responsible for allowing the front fork to rotate smoothly, enabling the rider to steer the motorcycle with ease. Steering head bearings bear both radial and axial loads, as they support the weight of the front end of the bike and help control its direction.
Types of Steering Head Bearings:
Ball Bearings: These are the commonly used bearings in steering heads, particularly in older or standard motorcycles.
Tapered Roller Bearings: Modern motorcycles, especially those with higher performance capabilities, often use tapered roller bearings in the steering head to provide better load distribution and enhanced durability.
The engine of a motorcycle is a highly complex system with many moving parts, and bearings are essential to reduce friction and allow smooth movement. Motorcycle engines typically use various types of bearings to support the crankshaft, camshaft, and other moving components.
Types of Engine Bearings:
Main Bearings: These bearings support the crankshaft in the engine and allow it to rotate with minimal friction. Main bearings are typically designed to handle heavy radial loads, as the crankshaft is one of the critical components in the engine.
Camshaft Bearings: These bearings are used to support the camshaft, which controls the opening and closing of the engine's valves. Camshaft bearings must be able to withstand the axial and radial loads generated by the camshaft's movement.
Ball Bearings: Ball bearings are commonly used for low to medium-load applications, especially in the camshaft and crankshaft areas.
Needle Bearings: Needle bearings are often used in small spaces within the engine to support rotational motion, such as in the transmission.
The clutch system in a motorcycle is responsible for engaging and disengaging the engine from the transmission, allowing the rider to shift gears smoothly. Clutch bearings play a significant role in enabling the clutch plates to engage and disengage without excessive friction. These bearings are often located within the clutch basket or between the clutch plates.
Types of Clutch Bearings:
Ball Bearings: Ball bearings are commonly used in the clutch assembly because they can handle both axial and radial loads efficiently.
Needle Bearings: In some motorcycles, needle bearings are used in the clutch system, especially in high-performance bikes where the clutch is subjected to higher stresses.

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español
