-
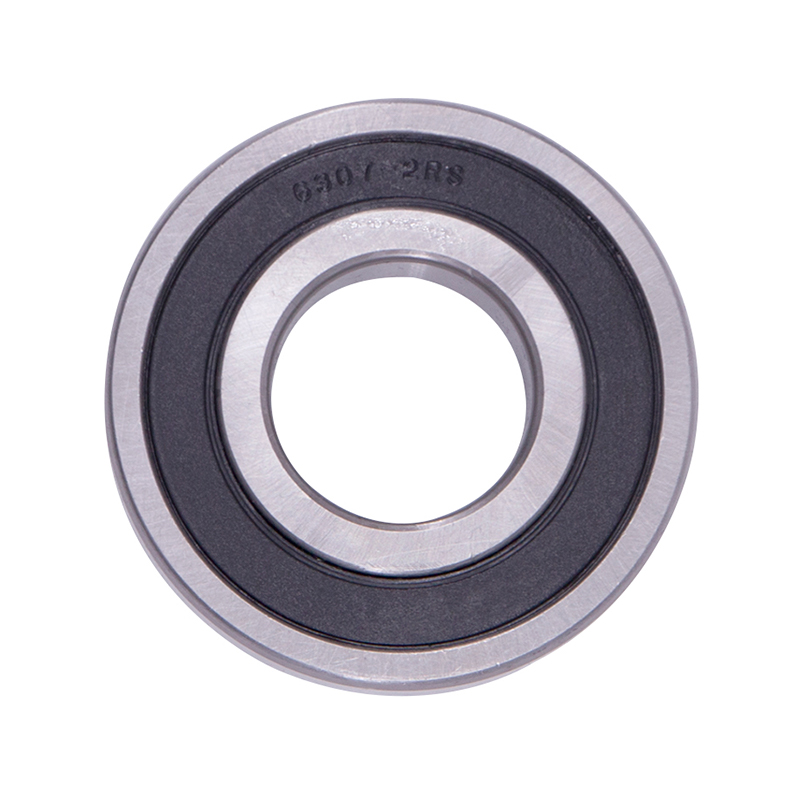 Wheel Hub Bearings
Wheel Hub Bearings -
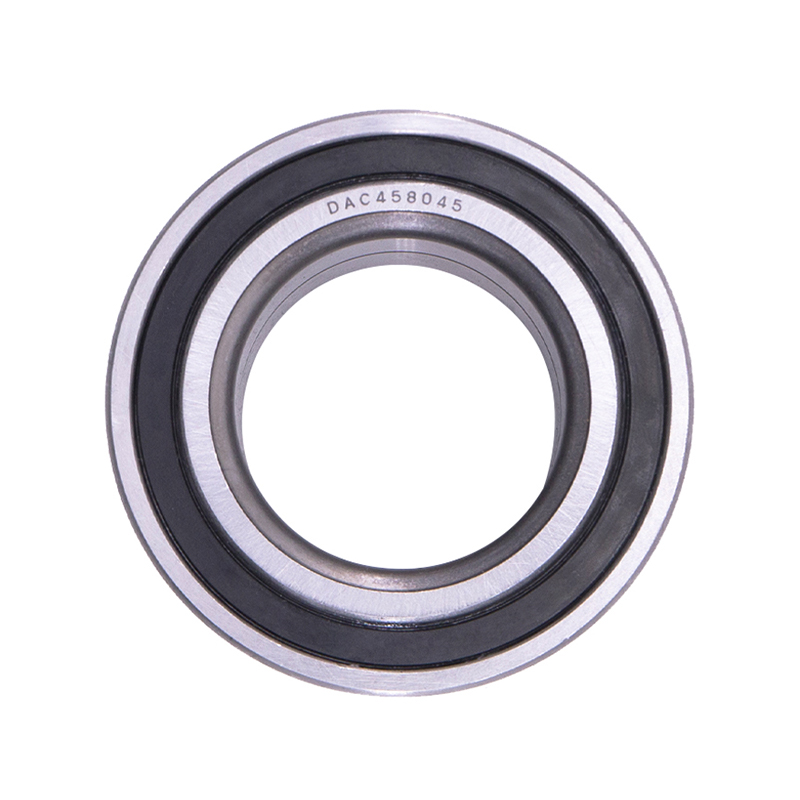 Wheel Hub Bearings
Wheel Hub BearingsDAC387436 DAC458045 Hub Deep Groove Ball Car Wheel Bearing
-
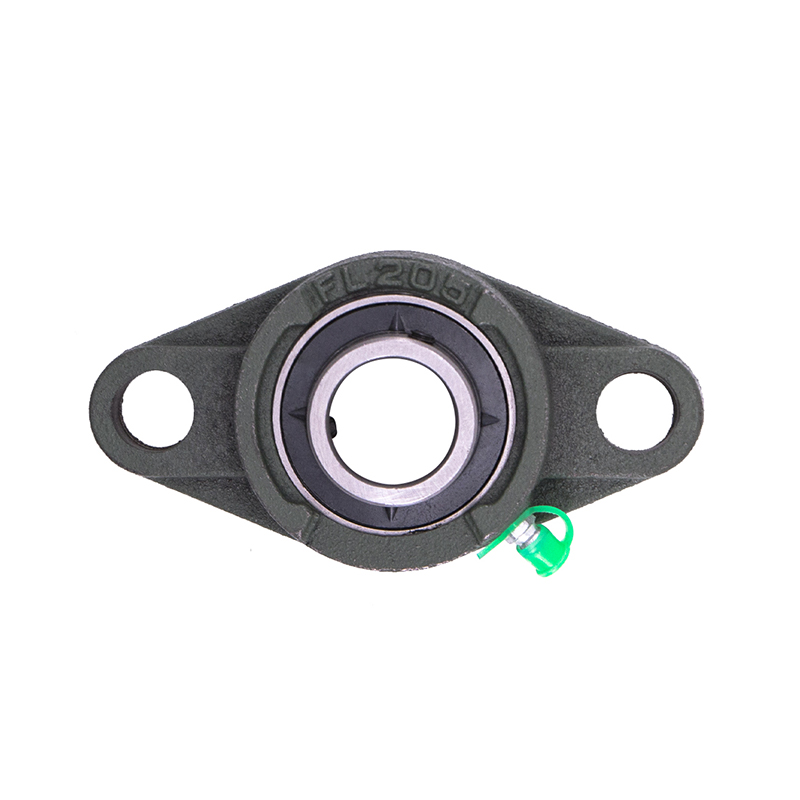 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsFL204 FL205 FL206 Stainless Steel Pillow Block Bearing
-
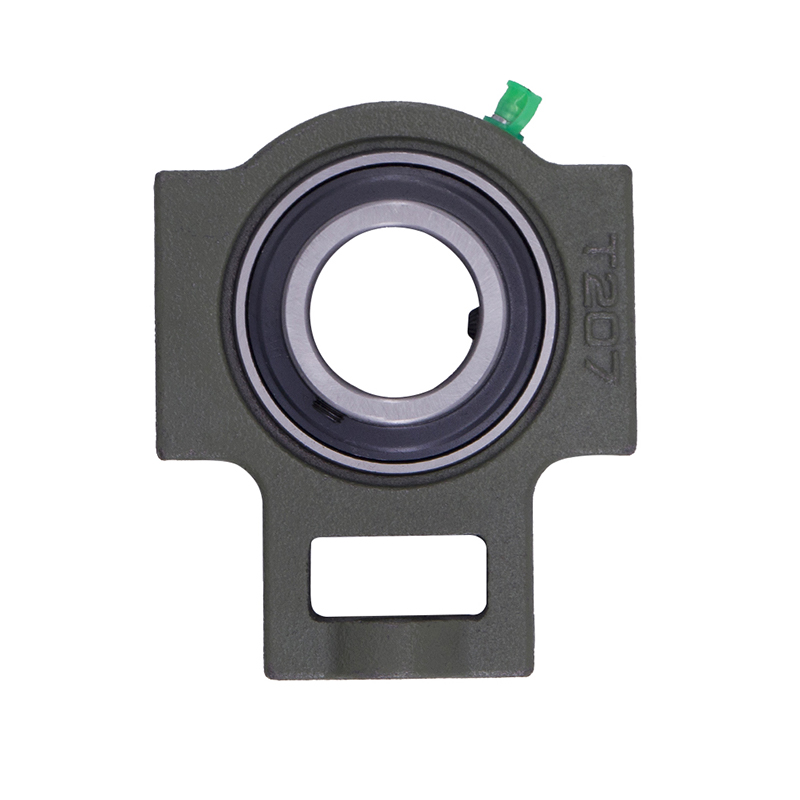 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsT204 T207 UC204 High Speed Insert Pillow Block Bearing
-
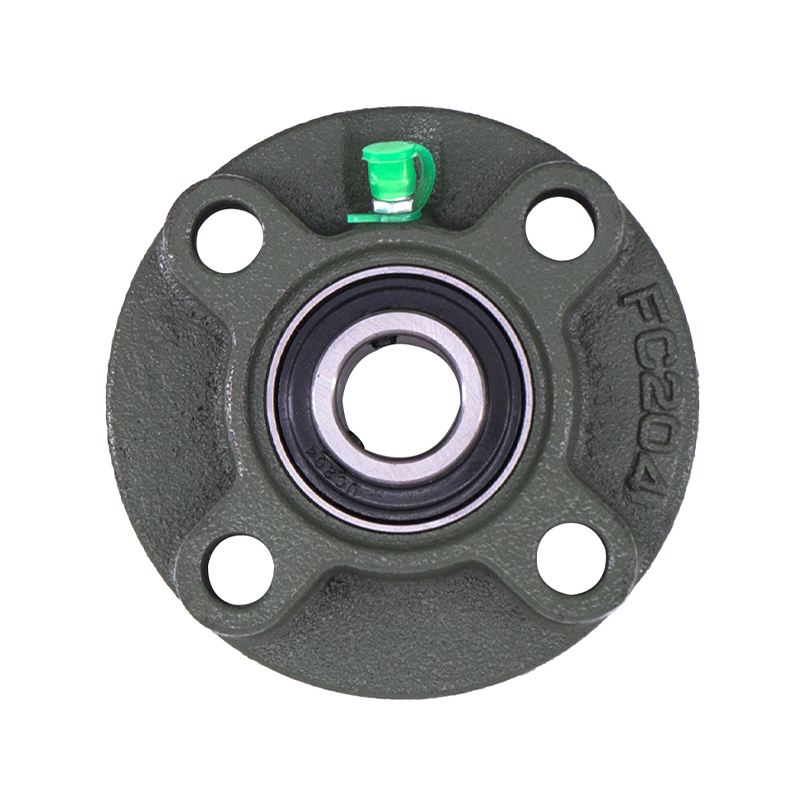 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsFC204 F210 Auto Wheels Bike Pillow Block Bearing
-
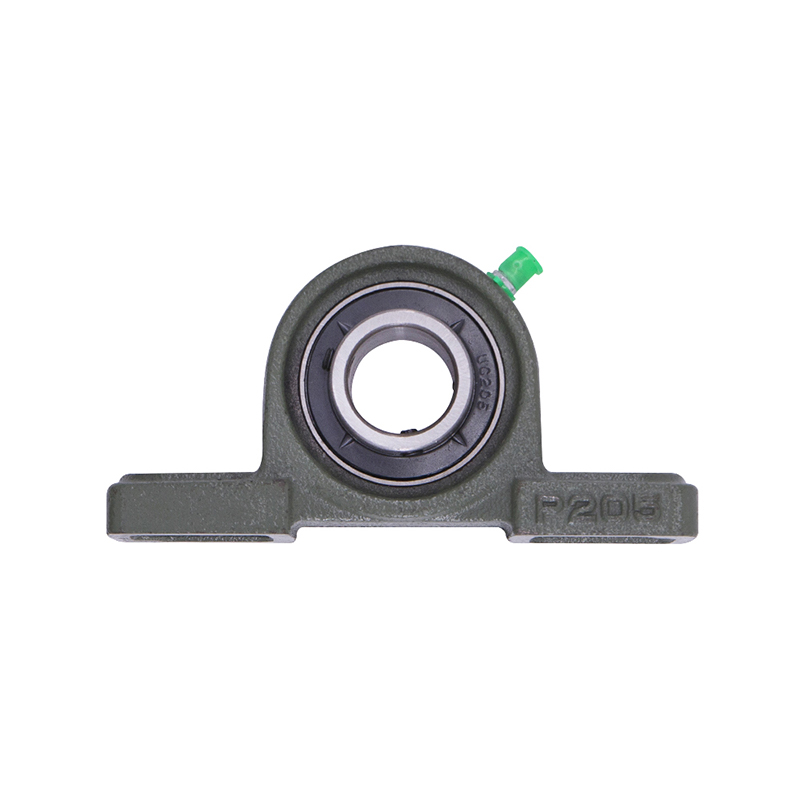 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsP207 206 205 203 High Precision Wheel Pillow Block Bearing
-
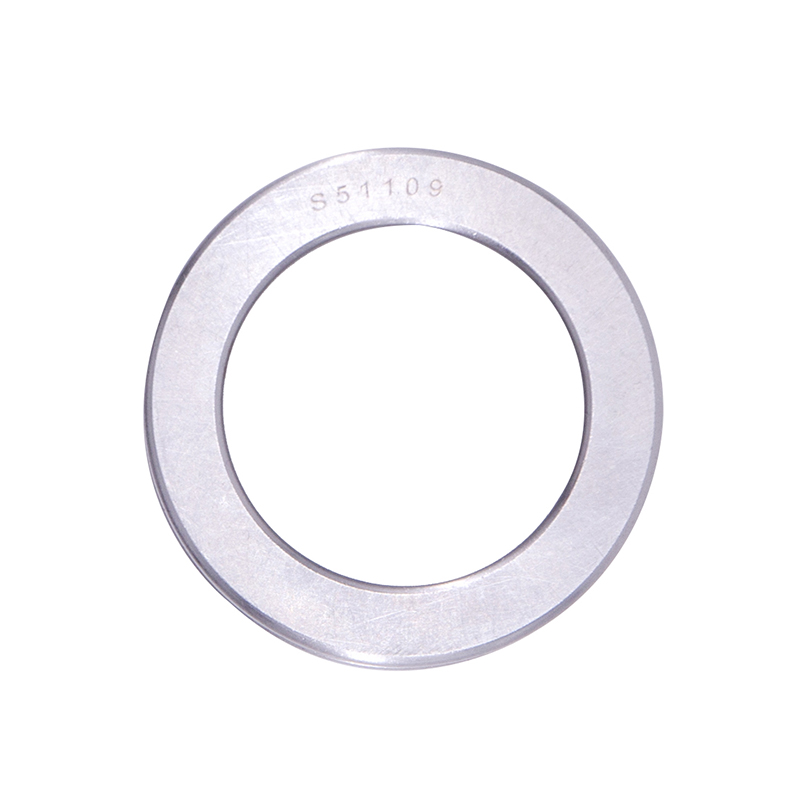 Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust Roller BearingsS51100 S51107 S51109 Car Wheel Plain Thrust Ball Bearing
-
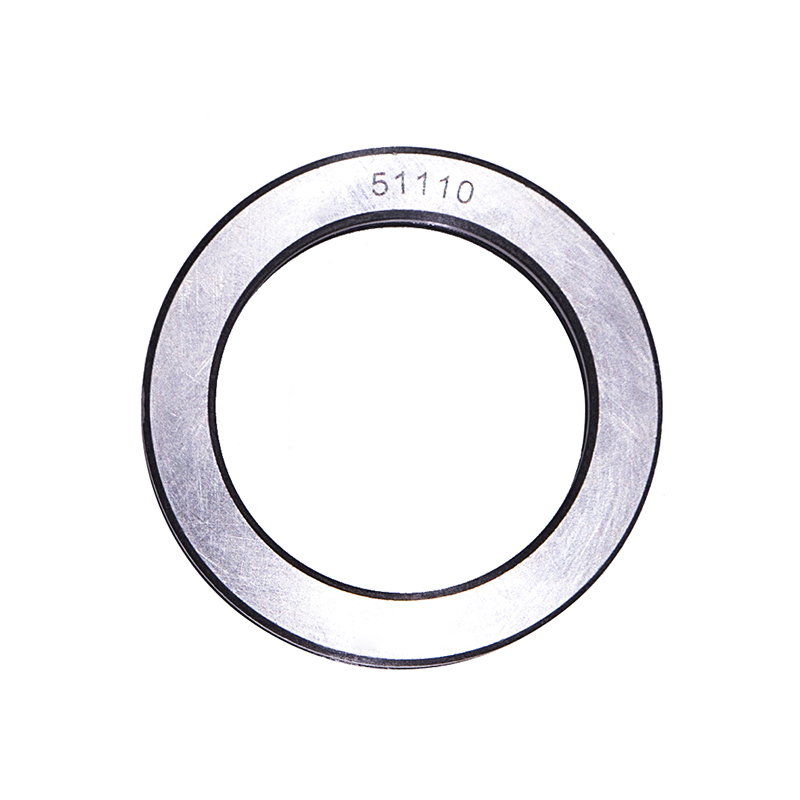 Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust Roller Bearings51110 51107 51104 51206 High Speed Plain Thrust Ball Bearing
The Development of Cylindrical Roller Bearings: A Journey of Precision and Efficiency
Industry news-Cylindrical roller bearings are vital components in modern mechanical systems, known for their ability to handle heavy radial loads and operate with minimal friction. These bearings are widely used in industries ranging from automotive to aerospace, heavy machinery, and manufacturing. Over the years, cylindrical roller bearings have undergone significant development, adapting to meet the increasing demands for efficiency, durability, and precision in various applications.

The concept of bearings dates back centuries, with the recorded designs appearing in the 18th century. However, cylindrical roller bearings, as we know them today, began to take shape in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The basic function of any bearing is to reduce friction between two surfaces in relative motion, allowing smoother movement and improved efficiency.
Cylindrical roller bearings were developed as a response to the need for bearings capable of handling radial loads, which occur when a load is applied perpendicular to the axis of the bearing. Unlike ball bearings, which use spherical rolling elements, cylindrical roller bearings use cylindrical rollers, which provide a larger contact area with the raceways. This design allows them to handle higher radial loads and operate at greater speeds compared to ball bearings.
Initially, cylindrical roller bearings were made from basic materials such as carbon steel. While effective in many applications, these early bearings had limited capabilities, particularly in terms of durability and resistance to wear. As industrialization progressed, so did the demands for more efficient, long-lasting bearings that could handle the increasing complexities of modern machinery.
One of the significant milestones in the development of cylindrical roller bearings was the improvement in the materials used for their construction. Early designs were primarily made from carbon steel, which provided adequate strength and wear resistance for many applications. However, carbon steel bearings often wore out quickly under high-stress conditions, limiting their lifespan and requiring frequent maintenance.
To address these limitations, manufacturers began experimenting with alloy steels, which incorporated elements such as chromium, manganese, and nickel. These alloys significantly enhanced the bearing's resistance to wear and fatigue, allowing them to handle higher speeds and heavier loads. The introduction of high-carbon chromium steel marked a major leap forward, providing a balance between strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance.
As technology continued to advance, the development of heat treatment processes further improved the performance of cylindrical roller bearings. Techniques like induction hardening and case hardening helped increase the hardness of the raceways and rolling elements, making the bearings more resistant to surface wear and fatigue.
Additionally, stainless steel became a popular choice for cylindrical roller bearings, especially in applications where corrosion resistance was critical. Stainless steel bearings are used in industries such as food processing, marine, and medical equipment, where exposure to moisture, chemicals, or high temperatures is common.
Alongside material advancements, the design of cylindrical roller bearings has evolved to accommodate a wide range of operating conditions and performance requirements. Early cylindrical roller bearings were simple, with minimal consideration for factors like load distribution and lubrication. However, as industries grew more specialized, so did the demand for bearings with specific design features that could handle varying loads, speeds, and environmental factors.
One of the important design innovations in cylindrical roller bearings has been the introduction of multi-row bearings. In certain high-load applications, such as in automotive axles or industrial gearboxes, multi-row cylindrical roller bearings are used to distribute the load across multiple rows of rollers, significantly increasing the bearing's capacity to handle both radial and axial loads. This innovation has made cylindrical roller bearings more versatile and efficient in heavy-duty applications.

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español
