-
 Wheel Hub Bearings
Wheel Hub Bearings -
 Wheel Hub Bearings
Wheel Hub BearingsDAC387436 DAC458045 Hub Deep Groove Ball Car Wheel Bearing
-
 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsFL204 FL205 FL206 Stainless Steel Pillow Block Bearing
-
 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsT204 T207 UC204 High Speed Insert Pillow Block Bearing
-
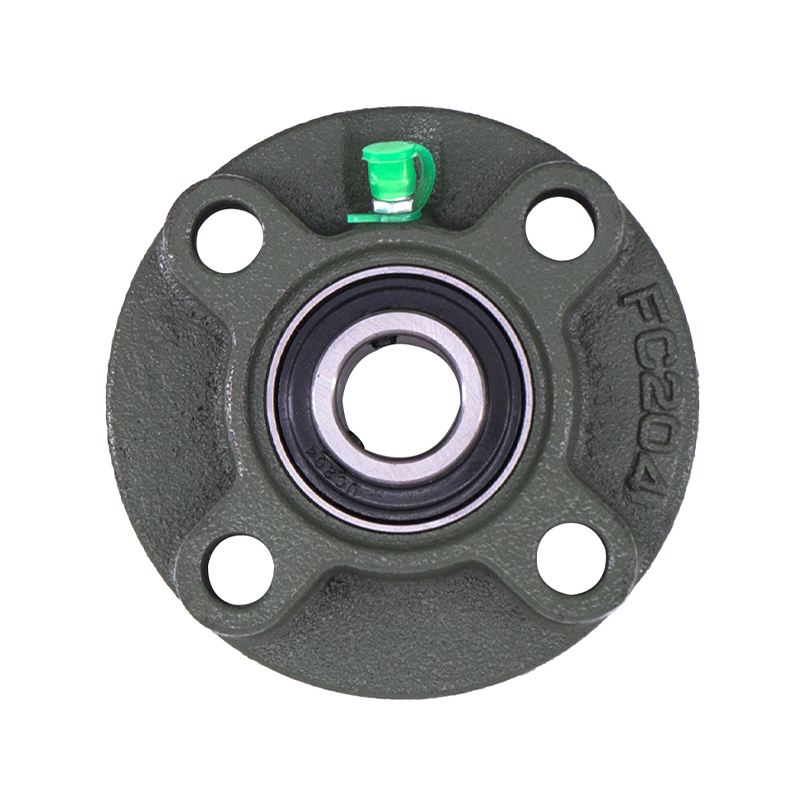 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsFC204 F210 Auto Wheels Bike Pillow Block Bearing
-
 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsP207 206 205 203 High Precision Wheel Pillow Block Bearing
-
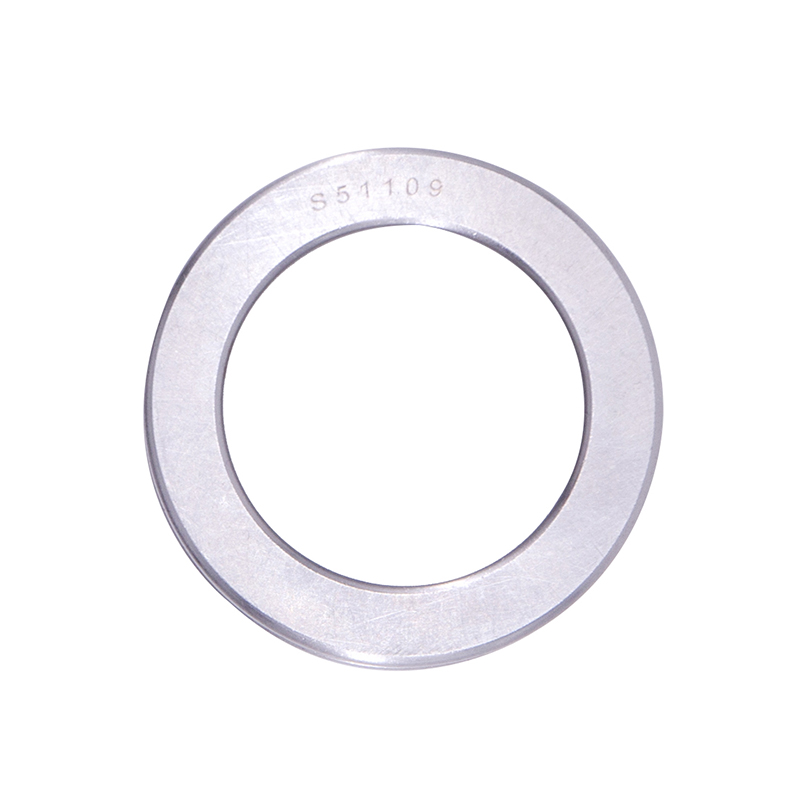 Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust Roller BearingsS51100 S51107 S51109 Car Wheel Plain Thrust Ball Bearing
-
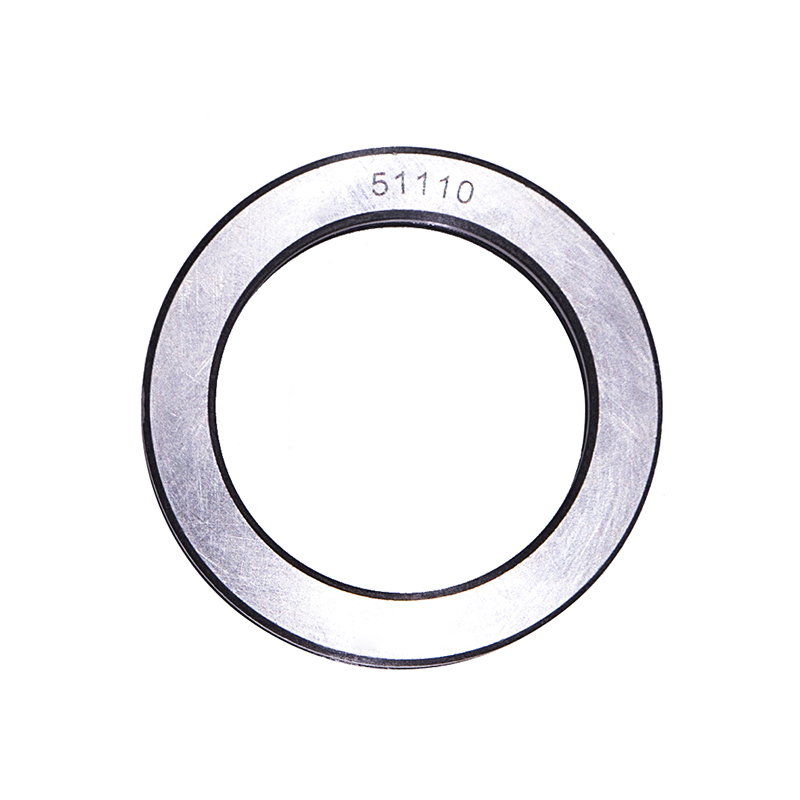 Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust Roller Bearings51110 51107 51104 51206 High Speed Plain Thrust Ball Bearing
High-Performance Motorcycle Bearing Overview
Industry news-Structural Design and Components
From a structural perspective, a high-performance motorcycle bearing consists of an inner ring, outer ring, rolling elements, and a cage or separator. The rolling elements are typically balls or rollers that facilitate smooth rotational movement by reducing friction between the shaft and housing. The cage maintains consistent spacing between the rolling elements, ensuring even load distribution and reduce wear over time. Bearings designed for motorcycles are often constructed from high-quality steel or stainless steel, with precision machining applied to the raceways and rolling elements. Some bearings include seals or shields to protect against contaminants such as dust, dirt, or moisture, which is particularly important given the outdoor and high-vibration conditions that motorcycles operate in.

The design may also vary depending on the application within the motorcycle. For example, wheel bearings require both radial and axial load handling, whereas engine bearings focus primarily on supporting radial loads with high rotational speeds. The structural integrity and precise tolerances of these bearings contribute to stable performance and reliability throughout a motorcycle’s operational life.
Operational Function
The primary operational function of a high-performance motorcycle bearing is to enable smooth and efficient rotation of mechanical components. Bearings reduce friction between moving parts, allowing wheels, engines, and gear assemblies to rotate with minimal resistance. This helps maintain mechanical efficiency, which is essential for consistent power delivery and handling.
Bearings also support loads generated during motorcycle operation, including radial loads from weight and tire contact, as well as axial loads from turning and braking forces. By evenly distributing these loads across the rolling elements and raceways, the bearing prevents excessive stress on individual components and minimizes wear. Additionally, sealed bearings retain lubrication, which supports smooth operation and reduces the risk of overheating or damage during prolonged use.
Applications in Motorcycle Systems
High-performance motorcycle bearings are used in several critical systems within a motorcycle. One major application is the wheel assembly, where bearings enable smooth wheel rotation and help maintain stability during turns, acceleration, and braking. In addition to wheel bearings, these components are applied in the engine, transmission, and steering assemblies.
Engine bearings support rotating shafts and connecting rods, ensuring consistent motion while reducing friction and heat generation. Transmission bearings facilitate gear rotation and torque transfer while maintaining alignment and durability. Steering head bearings support the front fork and handlebar assembly, allowing smooth and precise control. Each application requires bearings designed for the specific type of load, speed, and environmental exposure associated with that system.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
From a durability perspective, high-performance motorcycle bearings are designed to withstand vibration, shock loads, and environmental factors such as water, dirt, and temperature changes. Bearings are often pre-lubricated and sealed to maintain performance in these conditions. Proper maintenance, including periodic inspection and replacement when signs of wear or damage appear, helps extend bearing life and ensures safety.
Lubrication is essential for reduce friction and preventing overheating. While sealed bearings reduce maintenance needs, exposed or partially sealed bearings may require regular greasing, especially in high-stress applications. Correct installation is also crucial, as misalignment can cause uneven wear, reduce efficiency, and increase the risk of component failure. Routine checks for vibration, noise, or looseness can indicate potential bearing issues and help prevent mechanical problems.

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español
