-
 Wheel Hub Bearings
Wheel Hub Bearings -
 Wheel Hub Bearings
Wheel Hub BearingsDAC387436 DAC458045 Hub Deep Groove Ball Car Wheel Bearing
-
 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsFL204 FL205 FL206 Stainless Steel Pillow Block Bearing
-
 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsT204 T207 UC204 High Speed Insert Pillow Block Bearing
-
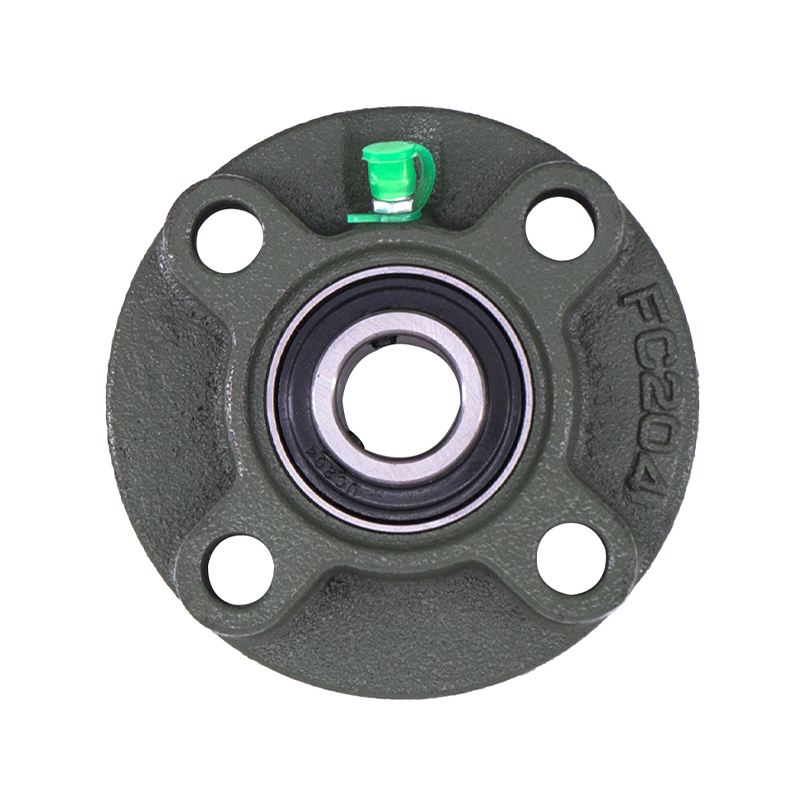 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsFC204 F210 Auto Wheels Bike Pillow Block Bearing
-
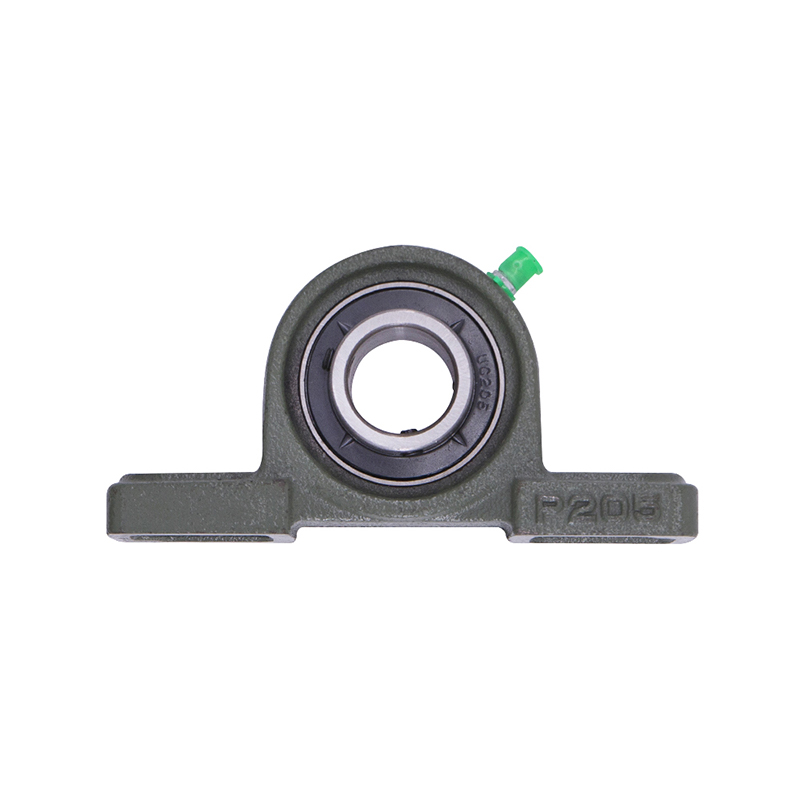 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsP207 206 205 203 High Precision Wheel Pillow Block Bearing
-
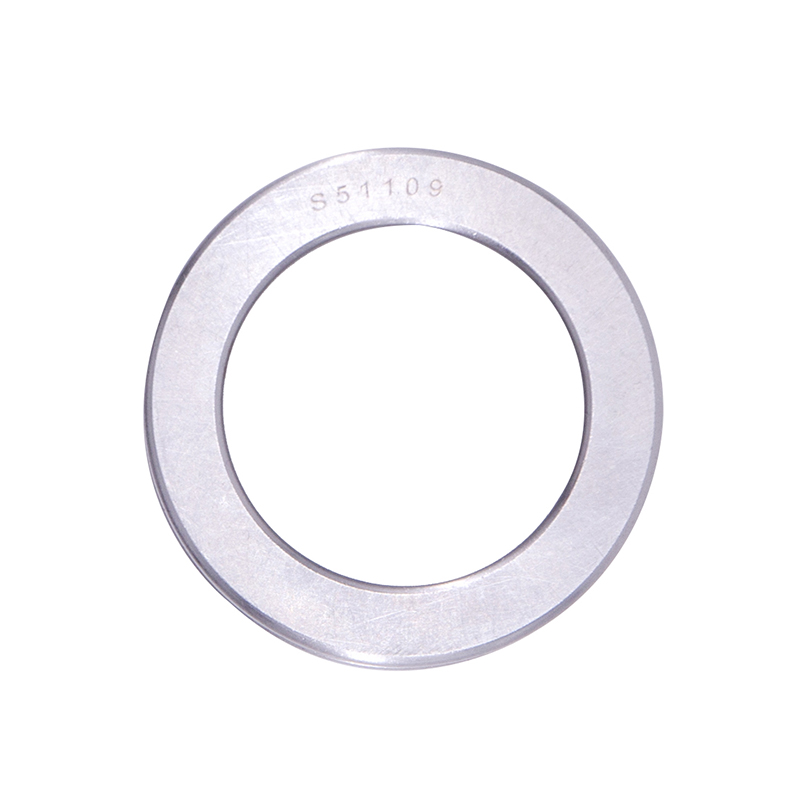 Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust Roller BearingsS51100 S51107 S51109 Car Wheel Plain Thrust Ball Bearing
-
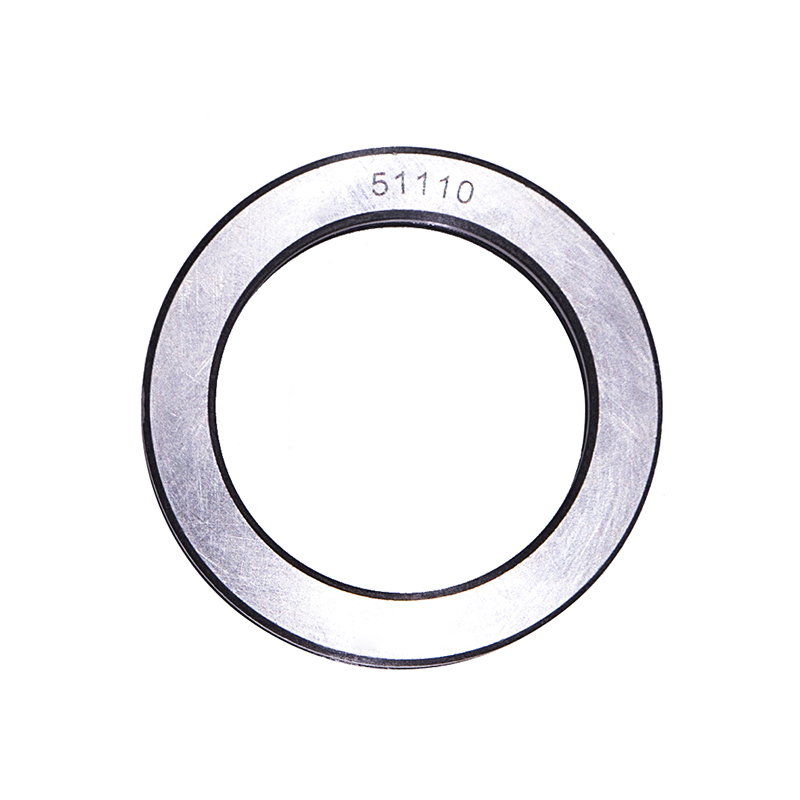 Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust Roller Bearings51110 51107 51104 51206 High Speed Plain Thrust Ball Bearing
How to Choose a Ball Bearing?
Industry news-Ball bearings factory are essential components in machinery and equipment, providing support for rotating shafts and reducing friction between moving parts. Choosing the right ball bearing is important for ensuring operational efficiency, stability, and longevity of the machine. Several factors, including load capacity, speed, precision, and environmental conditions, influence the selection process. The following sections answer four key questions to guide the choice of a ball bearing.

What Load Does the Bearing Need to Support?
The factor in selecting a ball bearing is understanding the type and magnitude of the load it will carry. Bearings experience both radial and axial loads. Radial loads act perpendicular to the shaft, while axial loads act parallel to the shaft. Some applications require a combination of both.
For light loads, standard single-row ball bearings are often sufficient, as they are designed to handle moderate radial and axial forces. For applications with higher radial loads or combined forces, double-row or angular contact ball bearings may be more appropriate. Determining the expected load ensures that the bearing can operate safely without deformation or premature wear. Consulting manufacturer load ratings for specific bearings helps match the bearing to the application.
What Operating Speed Will the Bearing Experience?
Another important consideration is the rotational speed at which the bearing will operate. Bearings generate heat and experience friction during rotation, and higher speeds require careful selection to prevent overheating and damage.
High-speed applications often require bearings with lower friction coefficients, precise machining, and lubrication systems suitable for maintaining stable operation. For moderate-speed operations, standard ball bearings may provide adequate performance. The choice of lubrication, either grease or oil, also depends on the speed, as it affects cooling and friction reduction. Evaluating the expected operational speed helps ensure the bearing maintains efficiency and longevity during use.
What Level of Precision Is Required?
Precision is an important factor for applications where accuracy and minimal vibration are necessary. Bearings are classified by precision grades, which define tolerances in diameter, roundness, and surface finish.
For general machinery, standard tolerance bearings provide adequate performance. For high-precision equipment, such as CNC machines, robotics, or instruments, higher-grade bearings with tighter tolerances are recommended. Precision affects noise levels, vibration, and the smoothness of rotation. Selecting the appropriate precision grade ensures that the machine performs reliably and meets operational requirements without excessive wear or energy loss.
What Are the Environmental Conditions?
Environmental conditions play a significant role in bearing selection. Factors such as temperature, humidity, exposure to dust, chemicals, or water, and the presence of corrosive agents determine the type of material, seals, and lubrication needed.
For standard indoor conditions, steel bearings with basic lubrication are often sufficient. For high-temperature environments, bearings made from heat-resistant steel or with special lubricants are preferred. In dusty or wet environments, sealed or shielded bearings help prevent contamination and extend service life. Understanding the operating environment ensures that the bearing maintains functionality and reduces maintenance requirements.
Choosing a ball bearing requires careful consideration of load capacity, operating speed, precision, and environmental conditions. Understanding the load ensures the bearing can support the necessary forces without damage. Considering the operational speed helps prevent overheating and friction issues. Evaluating precision requirements allows the selection of bearings that provide smooth, accurate rotation. Finally, assessing environmental conditions ensures protection against dust, moisture, and temperature variations.
By answering these four questions, manufacturers, engineers, and maintenance personnel can select ball bearings that are suitable for specific applications, ensuring reliable performance and extended service life. Proper selection also reduces operational risks, maintenance frequency, and potential downtime, making it an essential step in equipment design and maintenance. A careful evaluation of these factors allows for a more informed and practical choice of ball bearings.

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español
